The field of medicine is witnessing a groundbreaking development with the advent of “biobots”, microscopic robots made from human cells.
No larger than the head of a sharpened pencil, these biobots represent a new frontier in medical technology, bridging the gap between nanotechnology and traditional medical devices. Their potential impact on healthcare is significant, offering precise treatment options for a range of medical issues.
The Significance of Miniaturization in Medicine

The creation of biobots highlights the importance of targeting minute areas within the human body. Small-scale problems can lead to significant health issues, necessitating the development of tools that can operate at a micro level.
In the journal Advanced Science, Harvard biologists Mark Levin and his team explain the potential of small-scale interventions in effectively addressing medical challenges.
Anthrobots: Multicellular Robotic Innovations
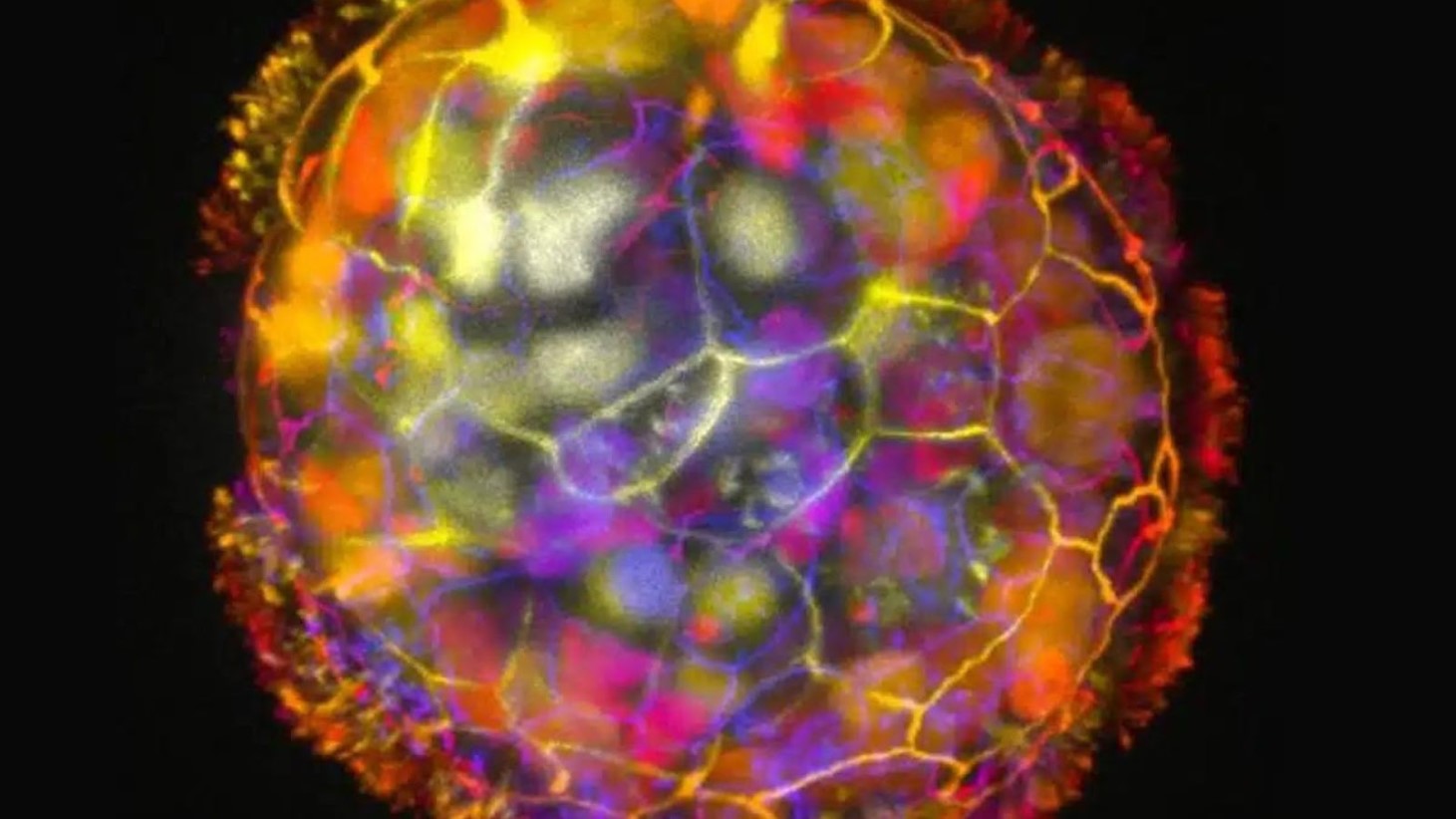
The research in Advance Science details how Harvard biologists have developed a new type of multicellular robot called “Anthrobots”, derived from human tracheal cells.
These biobots have been tested in laboratory settings where they successfully healed a simulated wound. This achievement showcases the potential of Anthrobots in medical applications, opening doors to new therapeutic methods.
From Science Fiction to Medical Reality
The study describes how Anthrobots, ranging in size from 30 to 500 micrometers, signify a leap from science fiction to practical medical application.
Unlike fictional robots, they are made from biological cells instead of metal and electronics.
The Composition and Lifecycle of Biobots
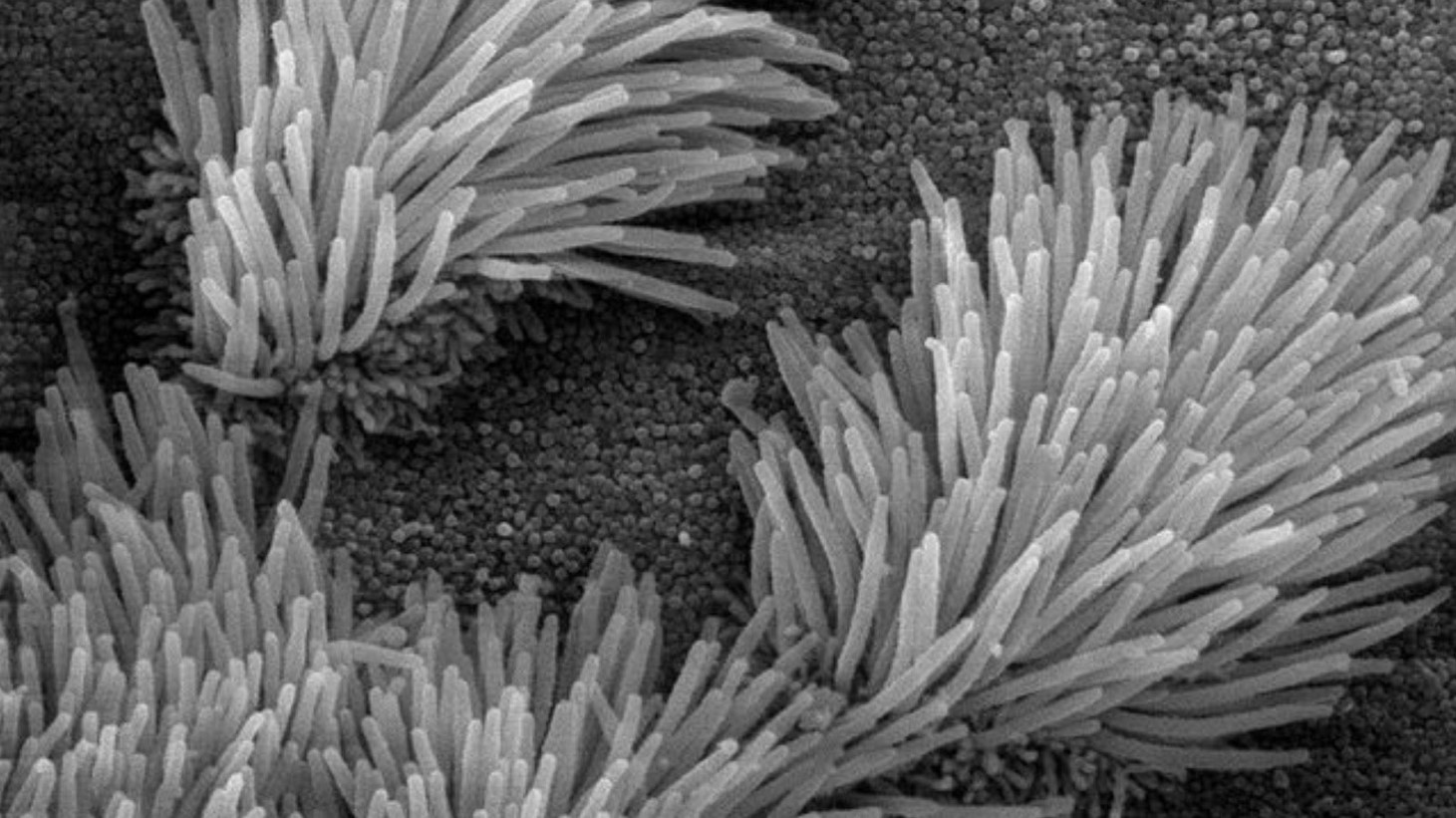

Anthrobots start as a single cell covered in cilia, resembling hair. These cilia are crucial for their movement and functionality.
In the lab, these Anthrobots naturally biodegrade after a period, showing their self-sustaining and environmentally friendly nature. This life cycle is a remarkable feature of these biobots.
The Healing Mechanism of Biobots
Mark Levin, in a press statement, expressed his fascination with the healing capabilities of Anthrobots: “It is fascinating and completely unexpected that normal patient tracheal cells, without modifying their DNA, can move on their own and encourage neuron growth across a region of damage.”
This natural healing process highlights the therapeutic potential of biobots.
Experimentation and Findings on Neuron Growth
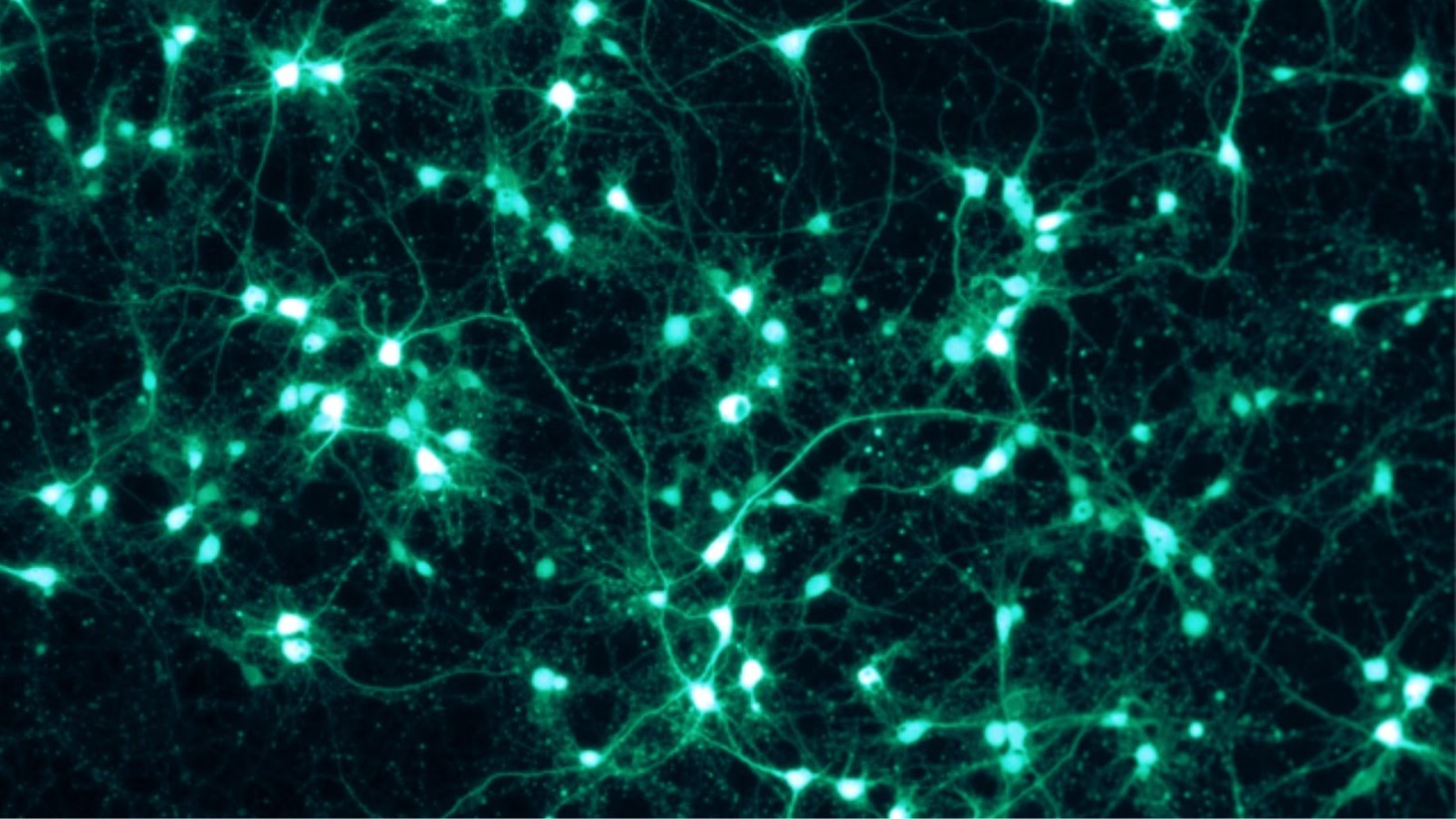
In the study, Levin and Harvard PhD student Gizem Gumuskaya created a 2D layer of human neurons and simulated a wound.
They introduced Anthrobots to the wound, where these biobots triggered neuron growth, essentially healing the simulated wound. This experiment provided significant insights into the healing capabilities of biobots.
Advancements Beyond Xenobots
Anthrobots represent an advancement over previous models like xenobots.
As Gizem Gumuskaya stated in a press release, “Unlike Xenobots, they don’t require tweezers or scalpels to give them shape… It’s fully scalable—we can produce swarms of these bots in parallel, which is a good start for developing a therapeutic tool.”
Potential Applications in Medicine
The successful healing of artificial wounds in laboratory settings is just the beginning for Anthrobots.
Their future development could lead to applications in clearing arterial plaque, repairing spinal cord damage, and other medical treatments. Their small size makes them ideal for these precise therapeutic applications.
Targeted Cancer Treatment Possibilities

The potential of Anthrobots in the fight against cancer is particularly promising.
Their ability to deliver drugs directly to targeted cells could revolutionize cancer treatment, offering a more efficient and targeted approach to battling this disease.
Scalability and Production of Biobots

The scalability of Anthrobot production is a key advantage.
As Gizem Gumuskaya highlighted in a press release, the ability to produce these biobots in large numbers simultaneously offers a significant step forward in developing them as therapeutic tools. This scalability is crucial for their widespread application in medicine.
Thoughts on the Future of Biobots
Anthrobots represent a significant innovation in the field of medicine. Their development marks the beginning of a new era in medical treatment, offering precise, targeted, and scalable solutions for various health issues.
As research and development continue, the potential applications and benefits of these biobots in healthcare are vast and promising.








































