Onions have been identified as a significant contributor to our health, thanks to their rich nutrient content.
Victoria Jarzabkowski, a nutritionist with the Fitness Institute of Texas at the University of Texas at Austin, emphasizes that onions are “super-healthy” and are excellent sources of vitamin C, sulphuric compounds, flavonoids, and phytochemicals. These components make onions not just a culinary staple but also a valuable addition to a healthy diet.
Understanding Phytochemicals and Flavonoids

Live Science explains that phytochemicals and flavonoids found in onions play a crucial role in promoting health. Phytochemicals are naturally occurring compounds that can trigger healthy reactions in the human body.
Flavonoids, responsible for the pigments in many fruits and vegetables, have been linked to reducing the risk of several diseases, including Parkinson’s disease and cardiovascular disease. These findings underline the importance of including onions in our diet.
The Role of Quercetin in Onions
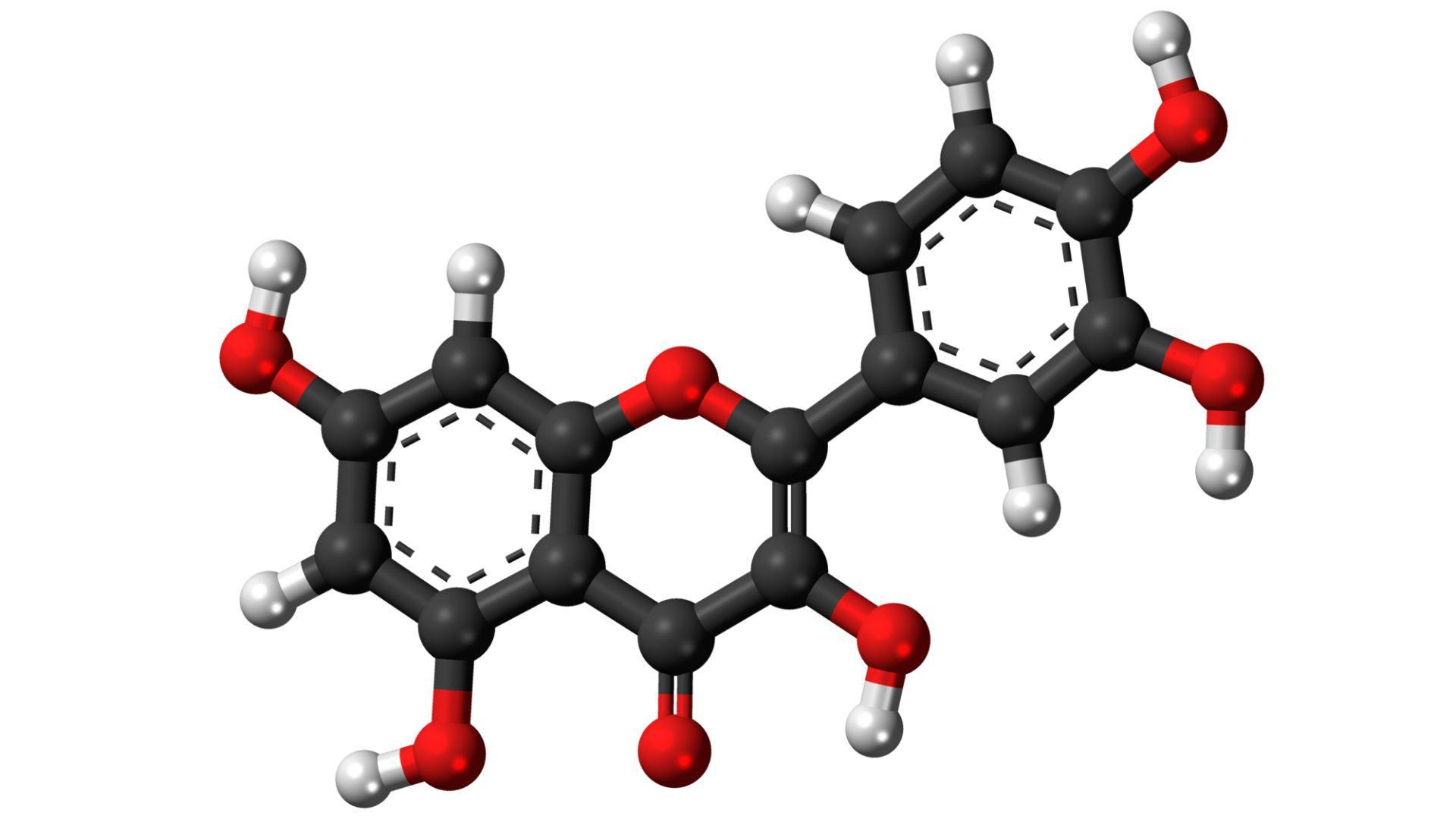
Quercetin is a flavonoid present in onions, known for its antioxidant properties. It has been linked to various health benefits, including the potential to prevent cancer, Live Science reveals.
Angela Lemond, a registered dietitian nutritionist, says that, “It also might have heart health benefits, though more studies need to be done.” Quercetin is also known for reducing symptoms of bladder infections, promoting prostate health, and lowering blood pressure.
Antioxidant Richness

The BBC notes that onions are among the most significant sources of antioxidants in the human diet.
According to Lemond, foods high in antioxidants and amino acids, like onions, enable the body to function optimally.
Antimicrobial Properties

The BBC reports that onions contain disulfides, trisulfides, cepaene, and vinyldithiins, phytochemicals with antimicrobial properties.
These compounds are beneficial in maintaining good health and have been recognized by the National Onion Association for their health-promoting effects.
Onions in Cancer Prevention
Research has linked the intake of onions to a reduced risk of certain types of cancer, illustrating their potential as a powerful food.
Despite these promising findings, it’s important to note that clinical trials are needed to fully understand the role of onions in this context.
Nutritional Profile of Onions

Onions are favored for their ability to add flavor without the addition of salt and sugar. Nutritionist Jarzabkowski highlights their low calorie, very low sodium, and no fat or cholesterol content.
Additionally, onions provide fiber and folic acid, a B vitamin that helps the body make healthy new cells, making them a nutritious choice for enhancing diet quality.
Onions and Heart Health
The consumption of onions has been associated with several heart health benefits, including the potential to lower blood pressure and reduce heart attack risk.
Live Science explains that their sulfur compounds act as a natural blood thinner, preventing blood platelets from aggregating and thereby reducing the risk of heart attack or stroke.
Managing Cholesterol with Onions

Research has also highlighted a relationship between the consumption of onions and the management of high cholesterol levels.
Onions increase oxylipins that help regulate blood fat levels and cholesterol, Live Science notes. This connection between onions and cholesterol management presents a compelling case for their inclusion in a heart-healthy diet.
Onions’ Impact on Inflammation and Immunity
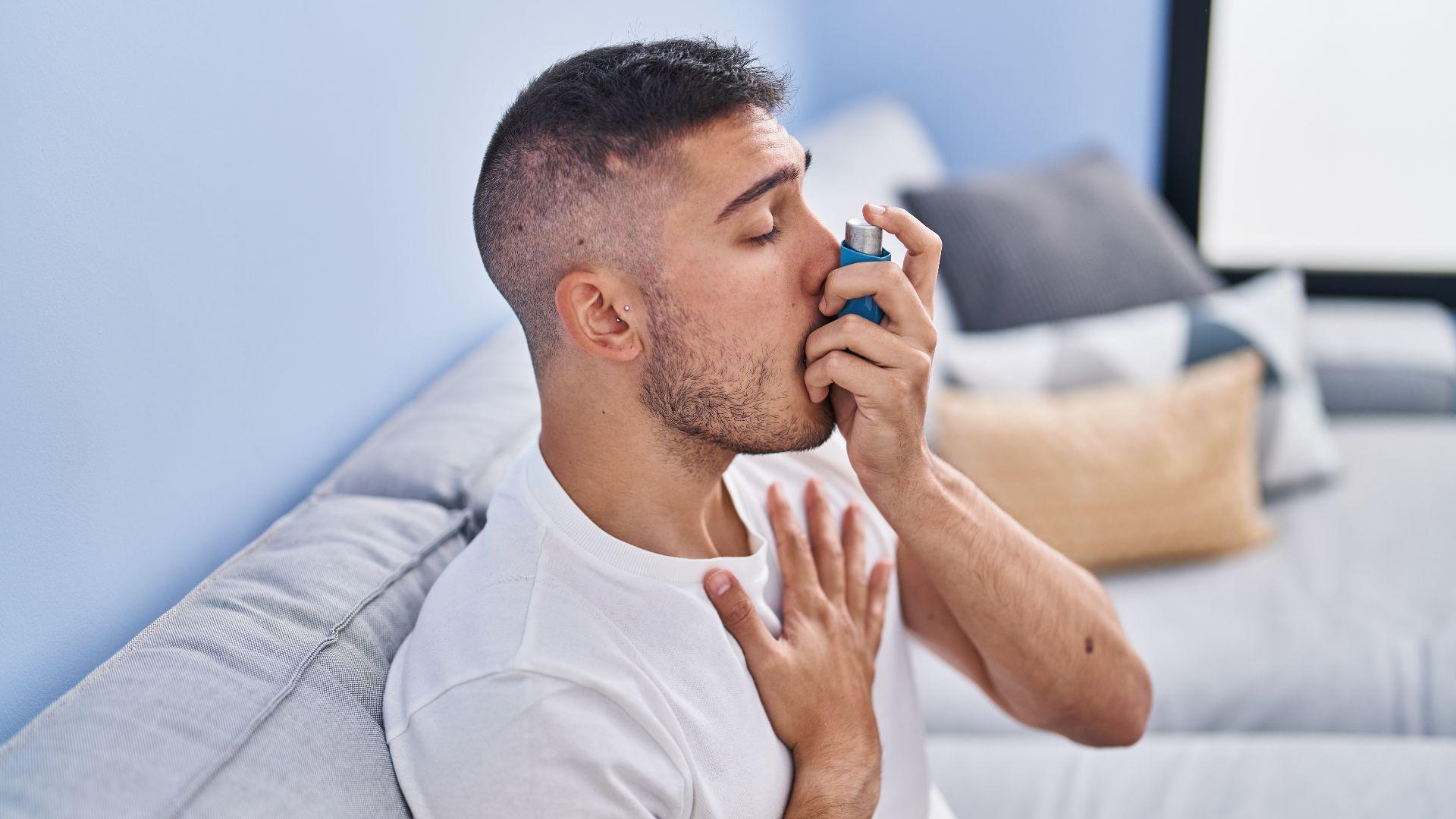

According to the BBC, onions have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, potentially offering relief for conditions like asthma.
Their sulfurs may act as effective anti-inflammatory agents, with quercetin found to relax airway muscles. Furthermore, the polyphenols in onions act as antioxidants, protecting the body against free radicals and supporting a strong immune system, as noted by dietitian Anne Mauney.
Onions’ Benefits for Digestion and Blood Sugar Regulation

Live Science explains that onions also contribute positively to digestive health and blood sugar regulation. Their fiber content promotes good digestion and regularity, while the chromium in onions assists in regulating blood sugar levels.
For individuals with diabetes, onions have been found to lower glucose levels, showcasing their potential as part of a dietary approach to managing diabetes.
Strengthening Bones with Onions
Research in the journal Menopause has shown that onions improve bone density, particularly in women who are post-menopausal.
Regular consumption of onions has also been linked to a lower risk of hip fracture, suggesting a role in combating osteoporosis and enhancing bone health.








































