While most people understand that gender inequality is still widely prevalent around the world and even in the United States, the true measure of this reality can be difficult to calculate.
Fortunately, researchers have developed a metric known as the Gender Inequality Index (GII) and have used it to determine which states have the best and the worst gender equality.
Understanding Gender Equality
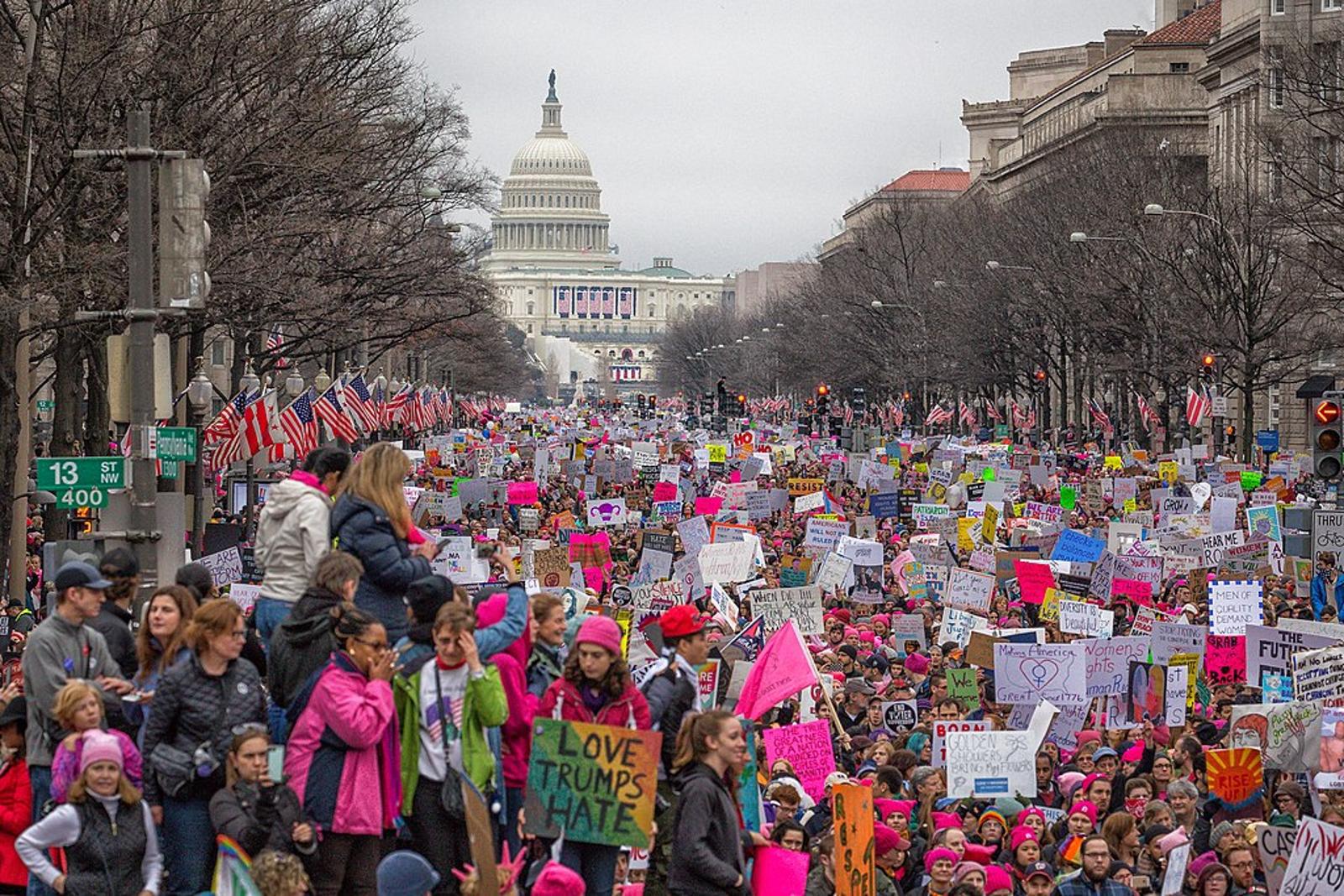

Gender equality is the idea that all people, regardless of their sex or gender, would be treated equally in society, culture, and legal matters. Conversely, gender inequality is when people are treated differently based on their sex or gender.
Gender inequality has seemingly always been a part of human life, and specifically, the gender inequality in our species has (almost) always favored men and discriminated against women.
Statistics Prove Gender Inequality

Researchers from New York University Abu Dhabi in the United Arab Emirates explained, “Gender inequality impacts numerous life domains, including health, labor-market participation, academia, and politics.”
The authors continued, “Women are systematically more likely than men to be victims of sexual harassment, are paid consistently less than men, and are less likely to be hired than men, especially in historically male professions.”
What Is the Gender Inequality Index?

However, while this is generally considered common knowledge, understanding just how much gender equality negatively affects women can be extremely challenging to measure, which is why they created the Gender Inequality Index or GII.
The GII takes maternal mortality, adolescent birth rate, parliamentary seats held by women, the percentage of women with secondary education, women’s participation in the workforce, women’s feeling of safety, life satisfaction, and financial well-being.
Applying the GII to the United States

When applying the GII metric to the United States, researchers noted a few interesting truths. First, the states with the highest GII rating, meaning the most gender inequality, also showed lower financial well-being for men.
This would indicate that gender inequality is directly linked to poor economic growth. Additionally, the study noticed that right-leaning states most often had less gender equality than left-leaning states.
Higher GII Scores Mean Less Awareness of Women’s Rights

The researchers also collected data from the social media platform X, formerly Twitter, to find out how the states’ GII scores correlated with their involvement in the #MeToo movement, which is a social, survivor-led campaign against sexual violence.
They reported that users from states with increased gender inequality had far fewer #MeToo posts, which they believe indicates that a higher GII score can result in lower levels of awareness and activism regarding women’s rights.
Map of Gender Inequality in the United States
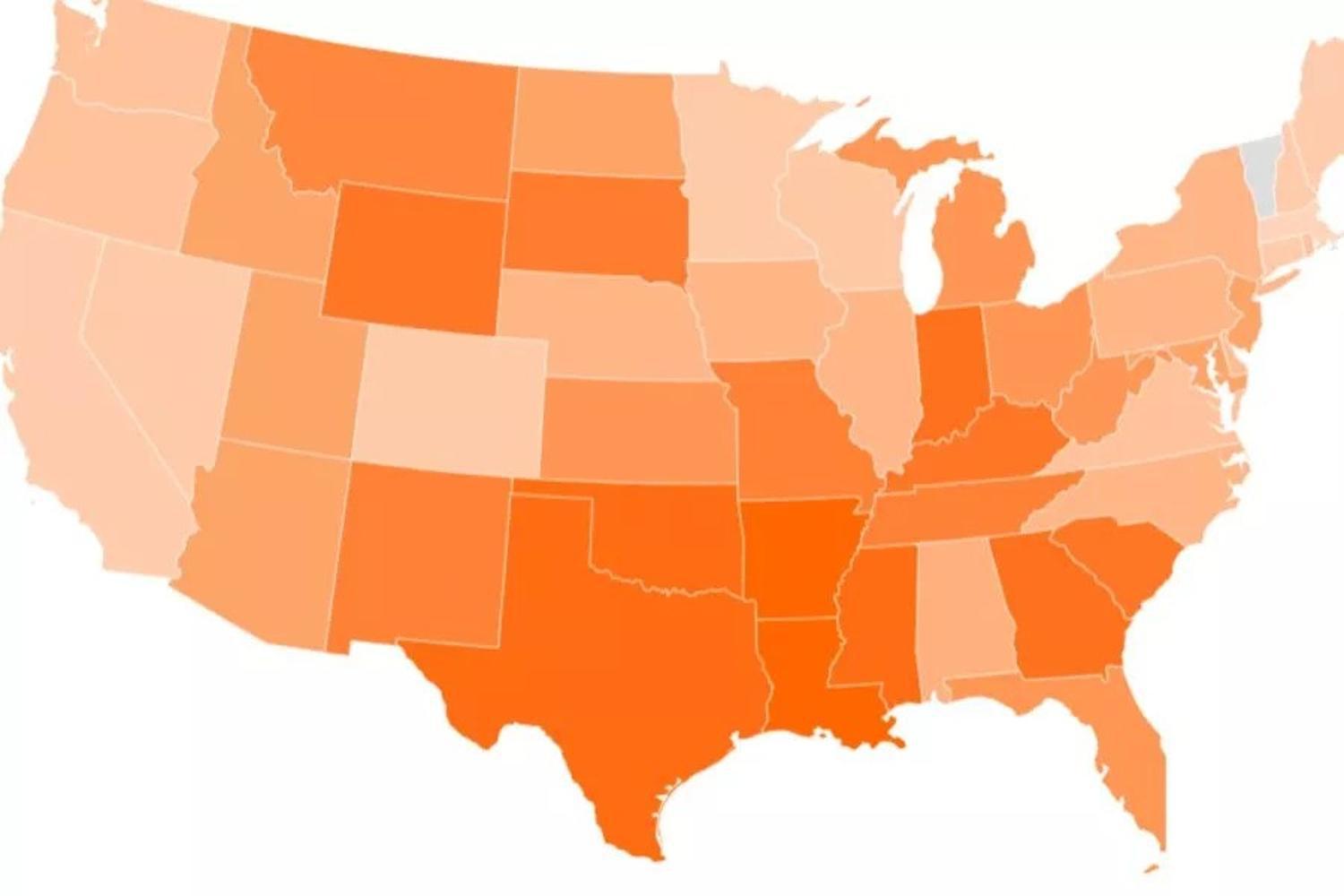
The GII metric only awards a score between zero and one; zero means the state has almost complete gender equality, and one means the state has extreme gender inequality.
A map was created to show the scores of each state with zero represented as light orange and states with a score of one in dark orange. The map shows that while some states sit somewhere in the middle, many states have drastic gender inequality.
States With the Worst Gender Inequality

According to the research, Arkansas, Louisiana, and Oklahoma have the worst inequality between men and women.
Unsurprisingly, these three states are among the ten poorest in the nation, with respective poverty rates of 16.8%, 18.6%, and 15.7%.
Gender Inequality Is Still Prominent in Texas, Mississippi, and Georgia

Mississippi, with a poverty rate of 19.1%, was also high on the GII scale, as were Texas, Georgia, and Indiana.
Each of these has elevated poverty rates of 14%, 15.6%, and 14.7%, respectively. While the poverty rate and GII score don’t directly correlate, there does seem to be a pattern in that states with increased poverty have less gender equality.
States With the Most Gender Equality
On the other hand, the states with the most gender equality include Massachusetts, California, and Maine, followed closely by Connecticut, New Hampshire, Nevada, and Colorado.
Massachusetts’s poverty rate is only 10.4%, but California’s is quite high at 13.2%. So, as the researchers reported, poverty seems to be influential but is certainly not the only determining factor.
Gender Equality Is a Pervasive Problem

The study’s authors explained, “Gender inequality is a pervasive global problem that affects rich and poor countries alike. A 2019 Oxfam report showed that nearly two-thirds of the world’s 781 million illiterate adults are women, a proportion that has remained largely unchanged for two decades.”
They continued, “Moreover, 153 countries’ legal systems still discriminate economically against women, including 18 in which husbands can legally prevent their wives from working,” the researchers wrote in the paper.
Gender Equality in the US Should Be Better

While most people understand that gender inequality exists, many are surprised to find just how prevalent it is in the United States.
The nation prides itself on being the land of the free for all people of every gender, but this study shows that, sadly, this is not the case. Women still struggle in many US states, especially those with poor economic growth.








































