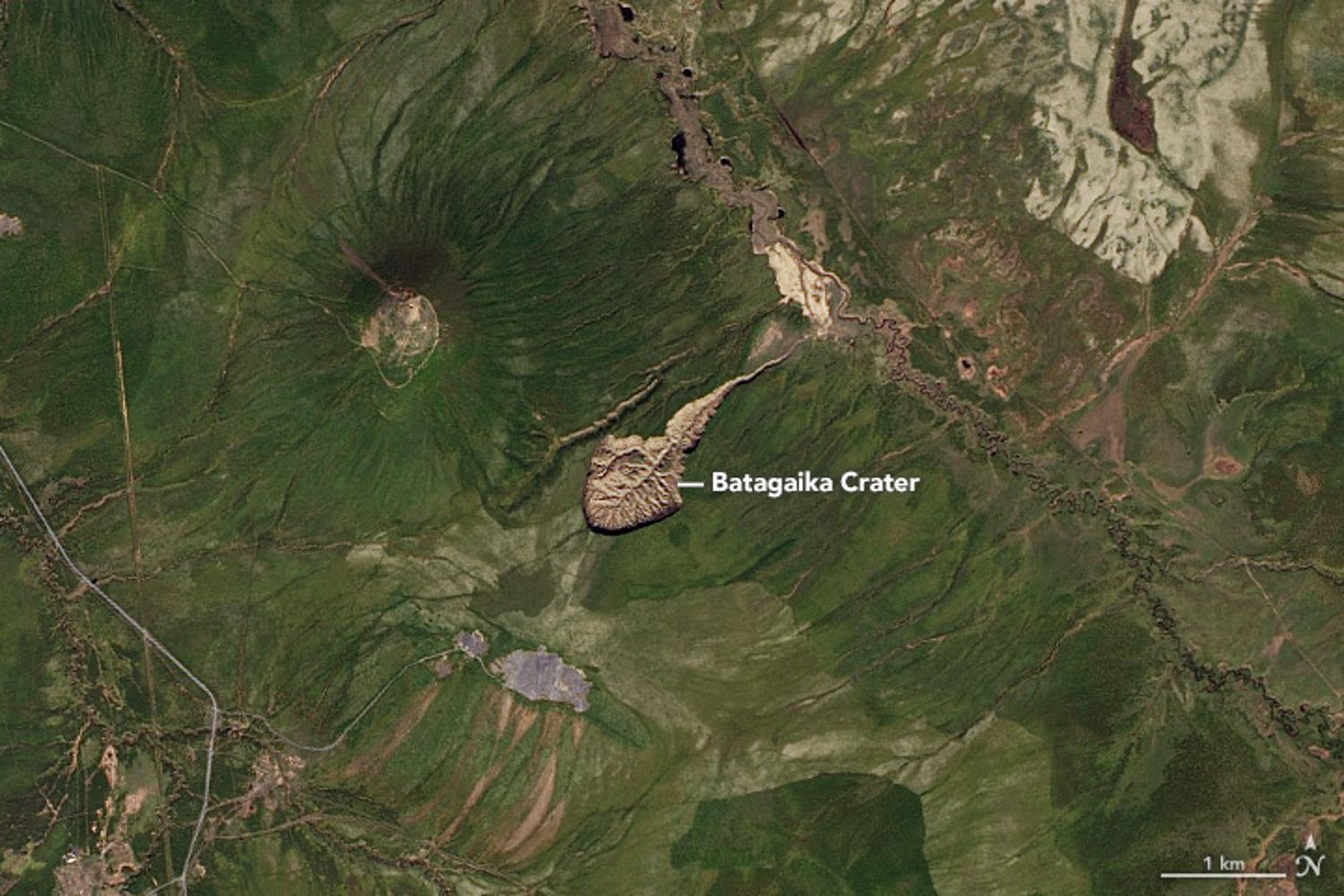
In Siberia, Russia, a once-small sinkhole has been quickly growing into a giant crater over the past 60 years.
The Batagay megaslump, better known as the “mouth to hell,” is growing at an alarming rate of between 10 and 30 meters every year, and experts say that climate change is undoubtedly to blame for the dangerous and ever-growing chasm.
The Beginning of the Batagay Megaslup
Before the Batagay megaslup was one of the largest sinkholes on Earth, it was simply a crack in the surface of the planet.
In the 1960s, a small crevasse appeared in the Yana Uplands of Northern Uakutia in north eastern Siberia, Russia. But over the past six decades, the crack has grown into a giant gash, one kilometer long and 328 feet deep.
How Did the “Mouth of Hell” Form?
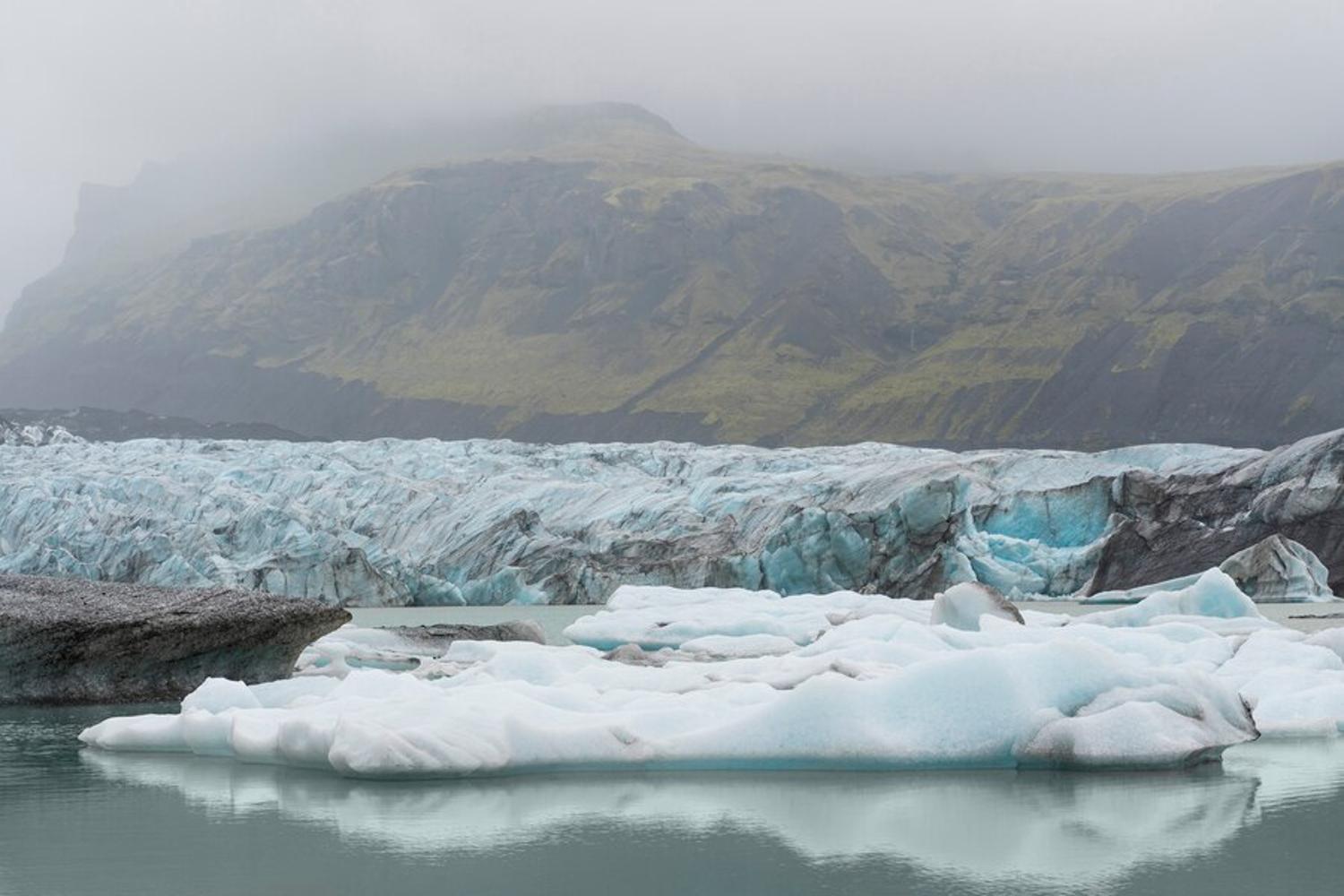

The land around the Batagay megaslump began sinking during an elongated thawing permafrost.
As the nearby icy tundra began melting extremely quickly, the land became excessively wet and weak. To make the situation even worse, the forest around the newly-formed crack had recently been cleared, leaving no natural protection for the wet soil to hold on to.
Erosion Is the Leading Cause in the Growth of the “Mouth to Hell”
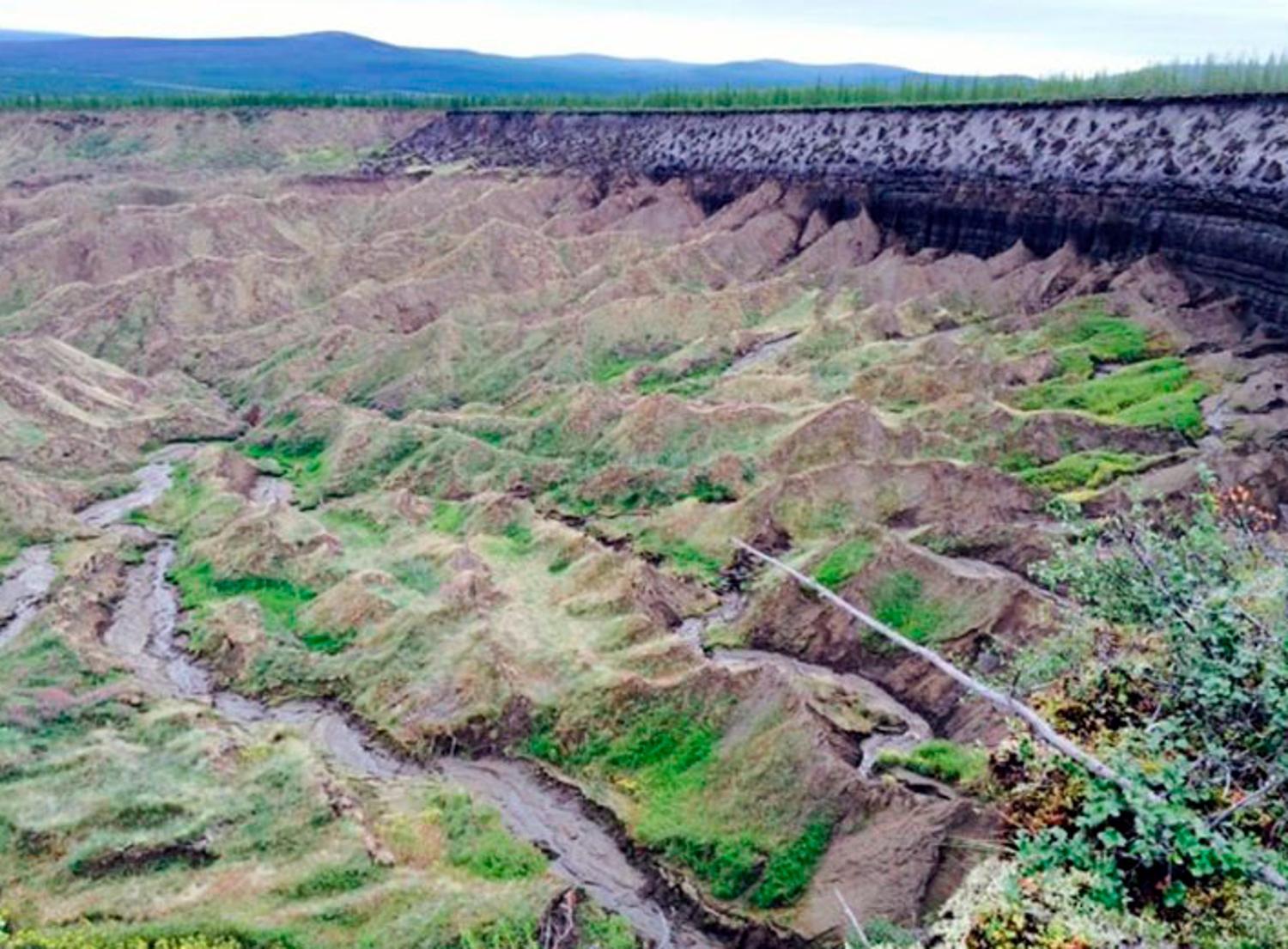

Although the soil is still vulnerable and moist, it is actually erosion that has led to the constant and extensive growth of the now-giant hole.
As Mary Edwards of the University of South Hampton explained, “Below the cliff face, steep hills and gullies drop to Batagaika’s floor. As more of the material at the bottom of the slope melts and comes loose, a larger face is exposed to the air, which in turn increases the speed of permafrost thawing.”
35 Million Cubic Meters of Soil Have Been Lost
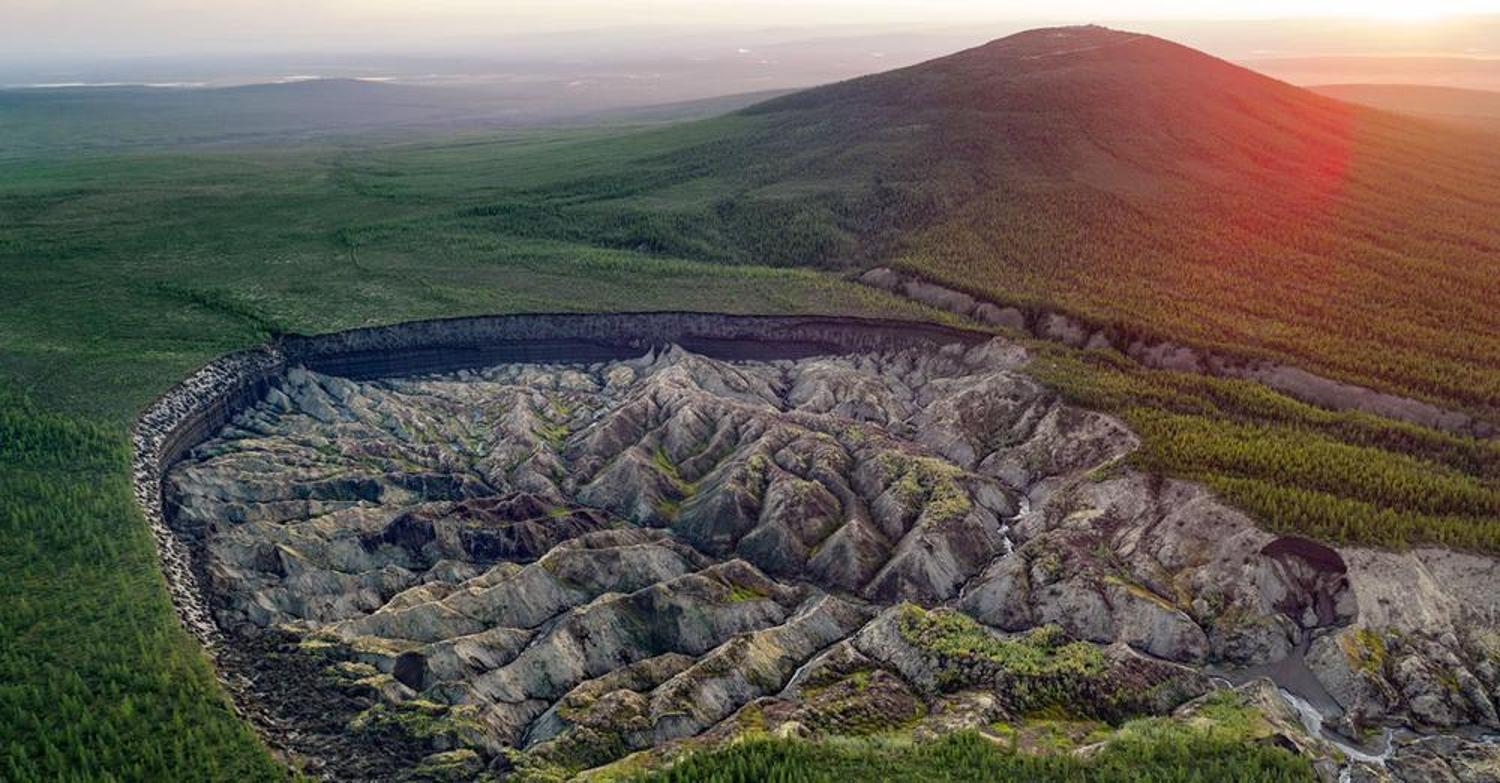

While the “mouth to hell” continued to collapse in on itself over the decades, over 35 million cubic meters of soil have been lost.
But experts believe the sinkhole isn’t done yet; it will continue to grow for the foreseeable future. A study from 2016 reported that the crater showed no signs of stabilization. On the contrary, it’s actually started expanding faster than ever before.
“It’s Very Hard to Stop It” From Growing
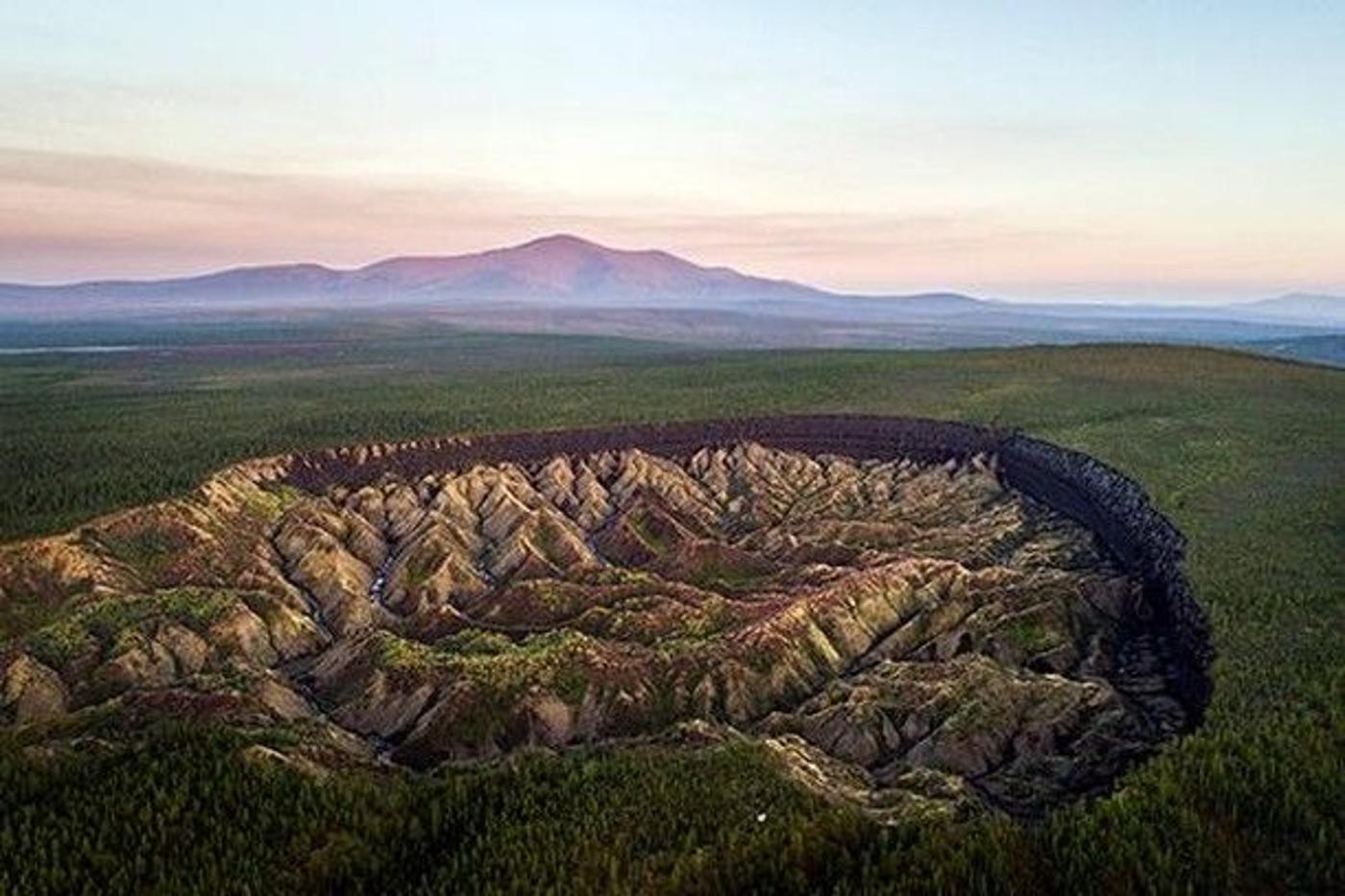

While many scientists have studied the fascinating and terrifying Batagay megaslump, no one quite knows how to stop it from growing.
Edwards explained, “The crater will likely eat through the entire hillslope before it slows down. Every year as soon as temperatures go above freezing, it’s going to start happening again. Once you’ve exposed something like this, it’s very hard to stop it.”
What Is Causing the Permathaw That Created the Batagay Megaslump?
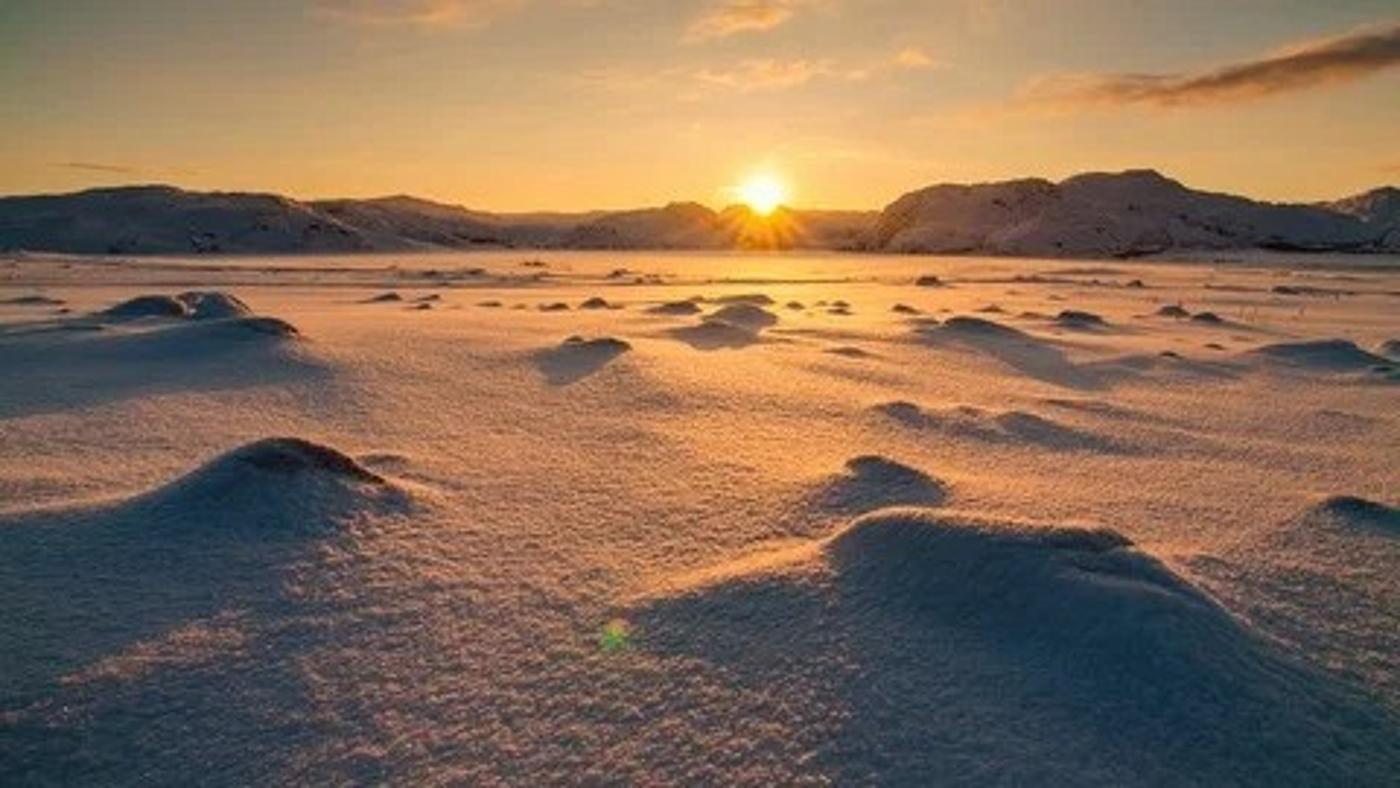

Although they don’t know how to stop it, they do understand why it happened in the first place. Scientists agree that the permathaw in the Siberian tundra that led to the creation of the “mouth of hell” was unquestionably caused by climate change.
Climate change has caused an intense warming of the planet’s oceans and atmosphere, both of which have led to excessive melting of ice in the far north. These areas, once covered with permafrost, are now experiencing permathaw, and melting rapidly.
The Excess Water Flows Straight Into the Ground
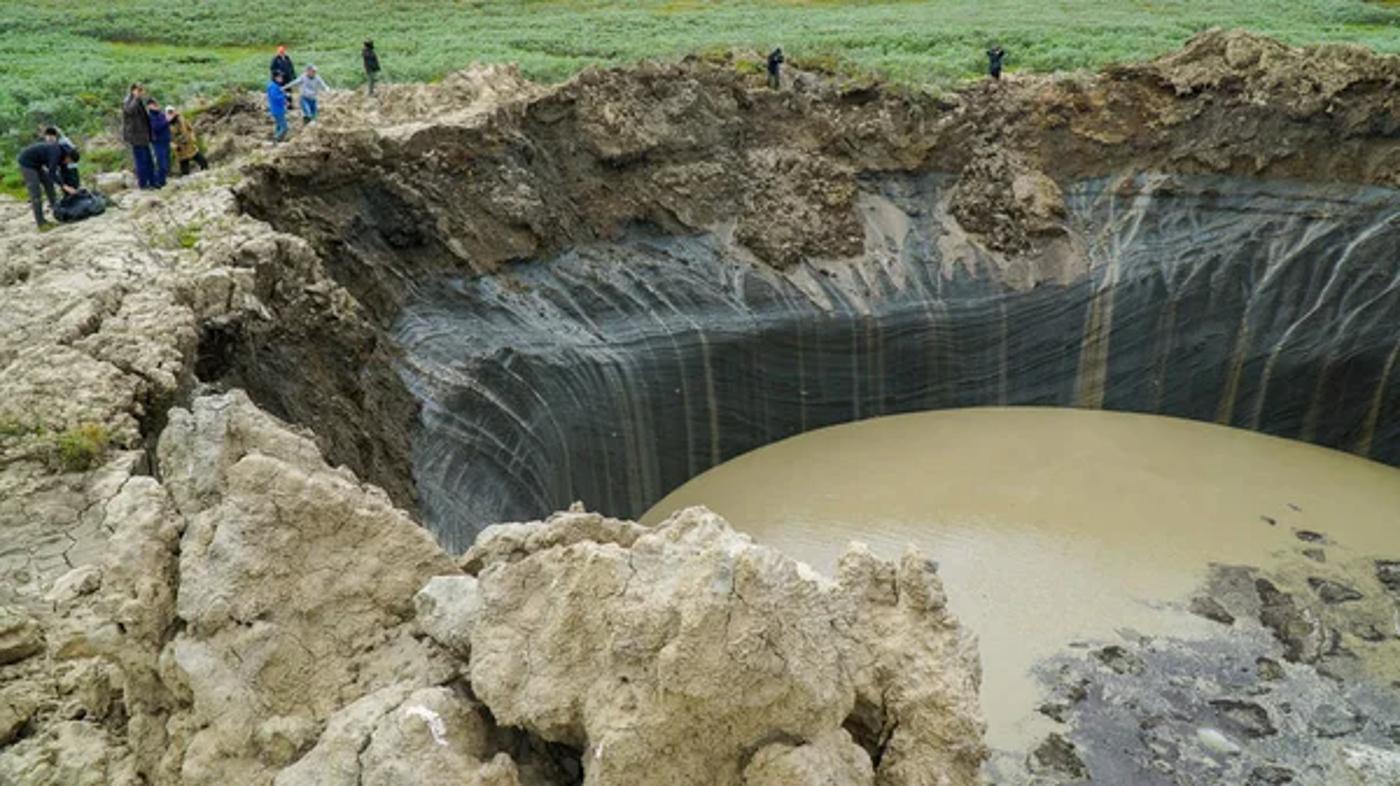

When these giant sheets of ice, some that covers hundreds of miles, begin melting, the excess water has to go somewhere. Of couse, if the ice sheets above the Arctic ocean, the water becomes a part of the Earth’s oceans.
But if the permafrost is on or near land, much of that water immediately permeates the soil below, destroying it’s natural composition and leaving destruction, often in the form of a sinkhole, in its path.
How Are Sinkholes Formed?

While the “mouth to hell” sink hole in Russia was created when permafrost melted, most other sinkholes form after excessive precipitation.
Extreme flooding can cause water runoffs that wet the soil to the point where it collapses in on itself, causing either a small or large sinkhole. While sinkholes are a natural occurrences, they are becoming more and more common for one big reason.
Sinkholes Are Becoming More Common All Over the World

When thinking of climate change, sinkholes don’t usually come to mind. However, they are yet another negative side effect of the rapidly changing configuration of the planet.
Melting ice in the far northernmost and southernmost poles has caused an influx of groundwater in certain regions, as has flash flooding and other extreme weather patters. All of which are consequences of climate change. The excess of water in the soil has led to the substantial increase of sinkholes all around the world.
Why Are Sinkholes Dangerous for the Planet?
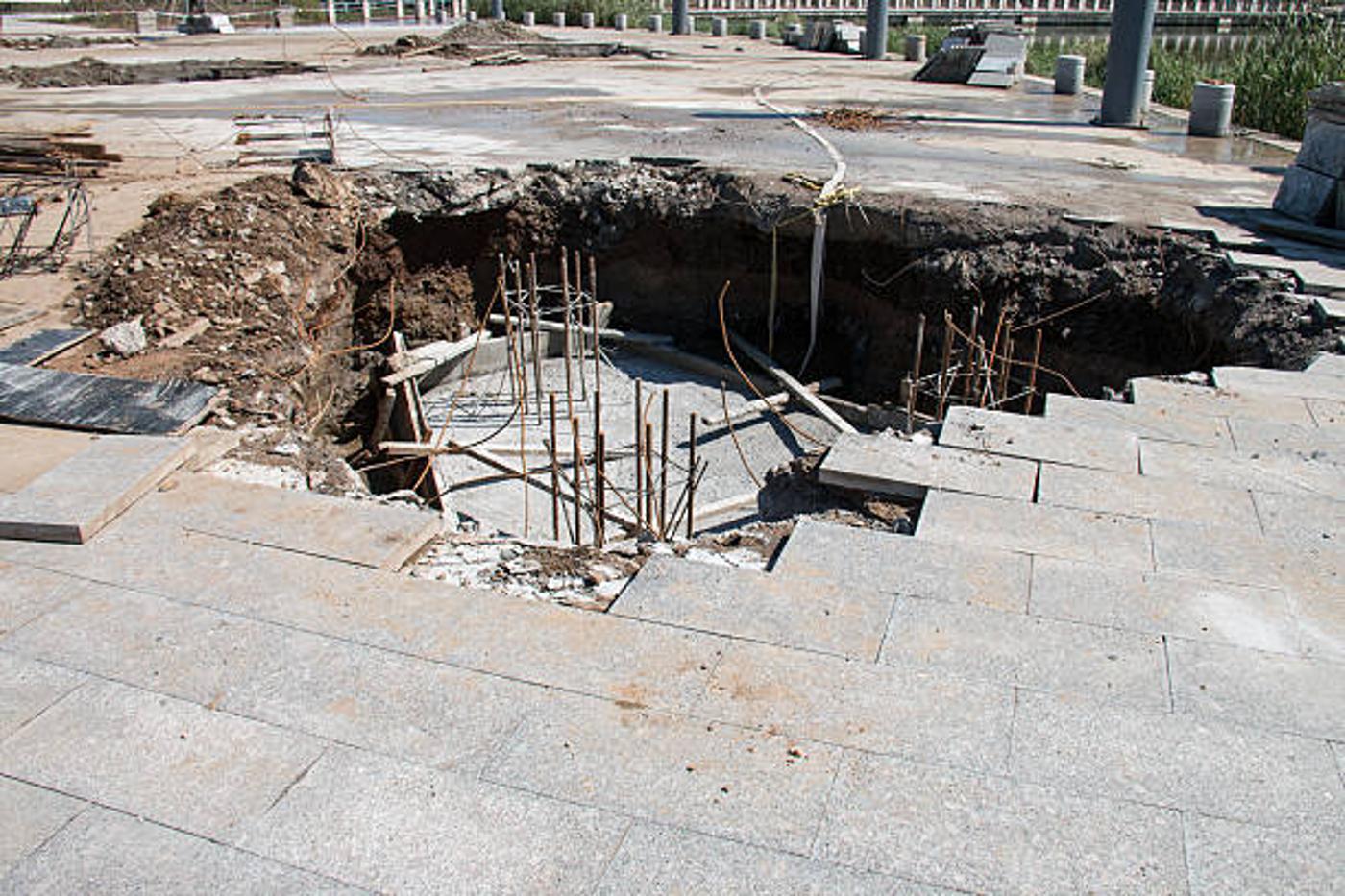

Rural sinkholes like the Batagay megaslump are extremely dangerous for the natural world around them. But sinkholes can appear absolutely anywhere, including under buildings and roads.
Because sinkholes often appear within seconds and without warning, anyone in the vicinity could be injured or even die before they realize the Earth is falling apart below them.
The Batagay Megaslump Is Just Another Example of the Planet’s Ongoing Struggles

Although sinkholes are technically a natural occurrence, chasms like the Batagay megaslump are not considered an ordinary event. There’s no doubt that this giant and dangerous sinkhole was caused by the rising temperatures due to climate change.
There are still some who hope that the “mouth to hell” will eventually stabilize; however, others argue it is unlikely. At this point in time, even if humans are able to save the planet from complete destruction, we will still have to live with current negative side effects of climate change as they are almost certanily irreversible.








































