Women are more likely to experience depression and anxiety compared to men, whereas men are more commonly diagnosed with autism and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). But scientists have long wondered why this is the case.
While several theories have been presented, including societal norms, underdiagnosis, and missed symptoms, medical researchers now believe they have a scientific answer.
Women Are Twice as Likely to Develop Anxiety

Studies show that women are at least twice as likely to develop anxiety or other mood disorders at some point during their lives as men are.
Additionally, doctors understand that women typically experience the side effects of certain medications, including antipsychotics and antidepressants, more than their male counterparts. However, they have never truly understood why.
Men Are Three Times More Likely to Be Diagnosed With Autism
Meanwhile, men are two times more likely to be diagnosed with ADHD and at least three times more likely to have autism.
And again, scientists and medical professionals haven’t had a concrete reason for these quite shocking statistics.
The Idea That Men and Women’s Brains Are Different Isn’t New Information
It’s not as though scientists don’t know that men’s and women’s brains work differently. While women’s brains are typically 11% smaller than men’s, even relative to their body size, female brains are typically far more active than male brains.
Men’s brains also contain more gray matter, which is associated with information and action, whereas women’s brains are composed of more white matter, which allows for higher-order thinking.
Research on Women’s Brains Has Only Advanced in Recent Years

However, this is actually quite new information. That’s because, for decades, most medical research was conducted on men.
As Dr. Ryan D’Arcy, a professor at the Center for Brain Health at the University of British Columbia, explained, “Brain imaging has historically largely collapsed females and males into the same sample, in spite of longstanding evidence that there are structural differences in female and male brains.”
Researchers Decided to Find Out Why These Differences Occur

In addition to the physical differences in men’s and women’s brains, there are also clearly emotional and intelligence differences.
So, scientists wanted to find out exactly how the brain’s microscopic cell structure affects the typical characteristics of males and females in life.
Scanning the Brains of 1,000 Young Adults

Researchers from the US and New Zealand conducted a study in which they scanned over 1,000 young adult brains to first identify the microscopic cellar differences in the regions of the brain that influence mental health, decision-making, emotion, and memory processing.
While their experiments were technically inconclusive, the scientists believe that two specific biological factors affected the physical development of the brains in these regions.
Hormones and Chromosomes

These researchers believe that hormones and chromosomes are both biological factors that affect the physical structure of brains in men and women.
Both men and women have estrogen and testosterone in their bodies. However, females have far more estrogen, whereas males have a great deal more testosterone. What’s interesting about these hormones is that they don’t only affect the physicality of a person but their brain chemistry as well.
How Do Hormones Affect the Brain?
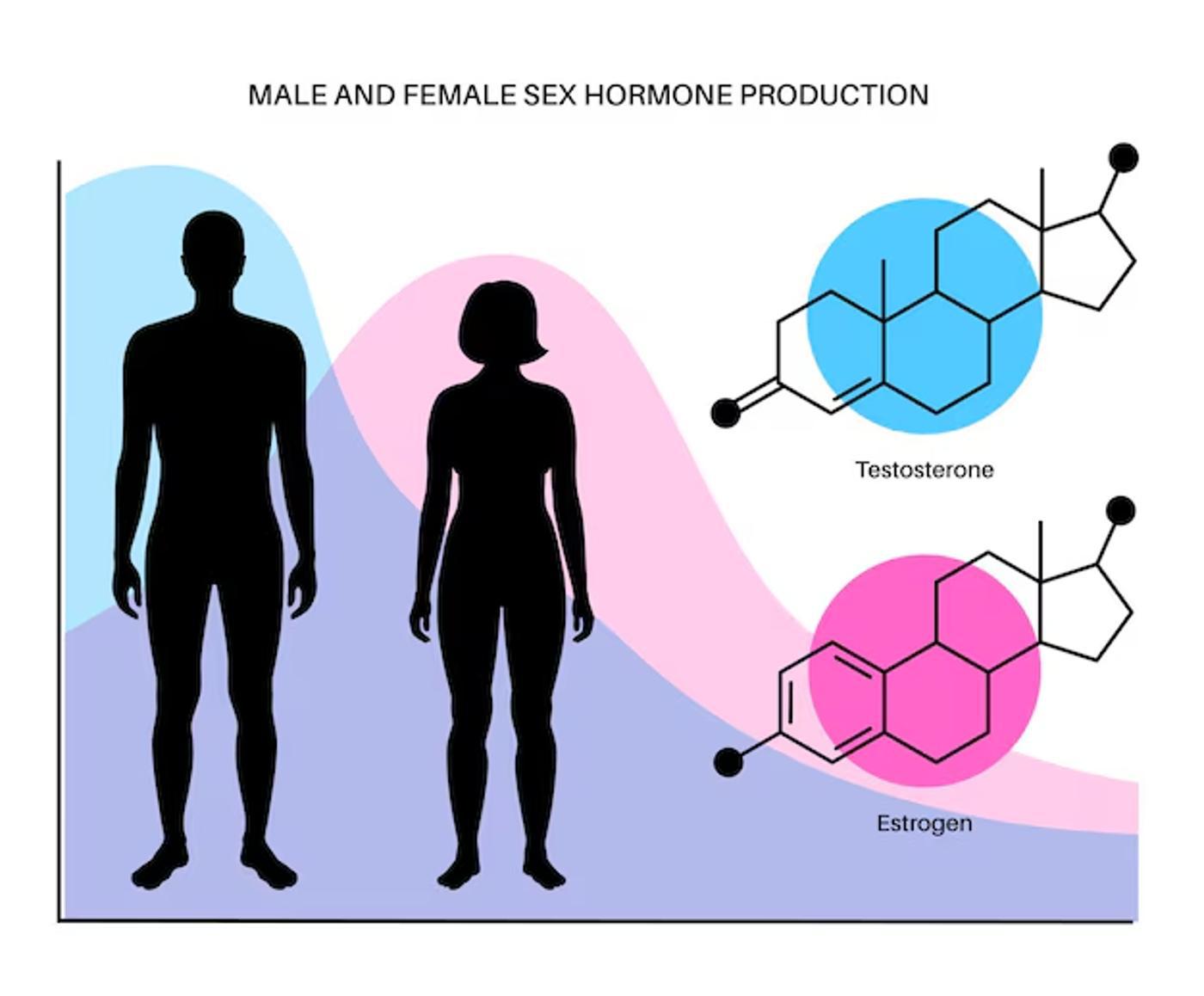
Most people understand how hormones affect the body. From puberty to menstruation, testosterone and estrogen are absolutely necessary. However, they also affect brain chemistry.
Estrogen helps with memory, concentration, and the processing of information, whereas testosterone affects the amygdala, which processes emotions and emotional responses.
How Do Chromosomes Affect the Brain?
Additionally, men and women have different chromosomes. Men have one X and one Y chromosome, but women have two X chromosomes.
A study conducted in 2021 showed that the X chromosome has a significant impact on brain anatomy, specifically the areas that determine thinking, action, and decision-making. Meanwhile, the Y chromosome actually increases brain size but doesn’t improve its functioning.
More Research Needs to Be Conducted

While this information is certainly interesting, more research needs to be done to say with absolute certainty that the brain’s physical structure is not only affected by the hormones and chromosomes in the body but also that these structural differences then lead to an increase in mood disorders in women and autism in men.
The hope is that, in the near future, scientists and, therefore, doctors will have a far better understanding of both the male and female brains.
Understanding the Differences Between Male and Female Brains Is Important

There are many reasons why this work is important, one of which is to enable medical professionals to help diagnose and understand the needs of both children and adults, specifically with their sex in mind.
If they can determine what makes brains act as they do, doctors will be able to diagnose and hopefully treat those experiencing these conditions with a more specific approach.








































