At this point, everyone is well aware that the use of fossil fuels, including coal and gas, is all but destroying the planet we live on. Therefore, scientists have been working desperately to find other, sustainable energy sources as quickly as possible.
While solar power, wind turbines, and electric batteries are steps in the right direction, there is a much more efficient way to power our world: Nuclear fusion. Until now, scientists haven’t been able to offer nuclear fusion that lasts more than several seconds, but now they can and it may change everything.
Fossil Fuels Are Not a Sustainable Energy Source

Fossil fuels, which include gas and oil, are an extremely unsustainable source of energy. Not only do they release toxic greenhouse emissions into the air when they are both produced and used, but they are also in limited supply.
The world will eventually run out of these resources, but by the time it does, the planet’s atmosphere may be so negatively impacted that Earth is no longer hospitable for human life.
The Green Energy Sources We Have Are Inefficient

Because of this terrifying reality, humans have attempted to find other sources of energy that won’t destroy the planet and will be available for generations to come.
But these sustainable green energy sources, like wind turbines and solar panel farms, are wildly inefficient. They are expensive to build and would have to take up an immense amount of space across the planet to provide the energy humans need to survive.
Harnessing the Energy of the Stars

Therefore, the most practical idea is to find a way to recreate the natural energy of the stars. The trillions of stars surrounding our planet, including the sun, are essentially giant balls of hot gases like hydrogen, helium, and various other elements.
As these elements squeeze together, their almost infinite nuclei squeeze together in a process called nuclear fusion to create massive amounts of energy. Now, humans want to find a way to produce nuclear fusion on Earth.
What Is Nuclear Fusion?

It’s crucial to understand that nuclear fusion is vastly different from nuclear fission. Nuclear fission is when the nucleus splits spontaneously, impacts another particle, and creates a burst of energy.
Whereas nuclear fusion is a planned reaction between two or more atomic nuclei which forms a new nuclei and subatomic particles that then create energy. The idea is that, if scientists can find a way to safely and continuously perform nuclear fusion, they will have a sustainable energy source forever.
Scientists Around the World Have Created Six Types of Fusion Reactors
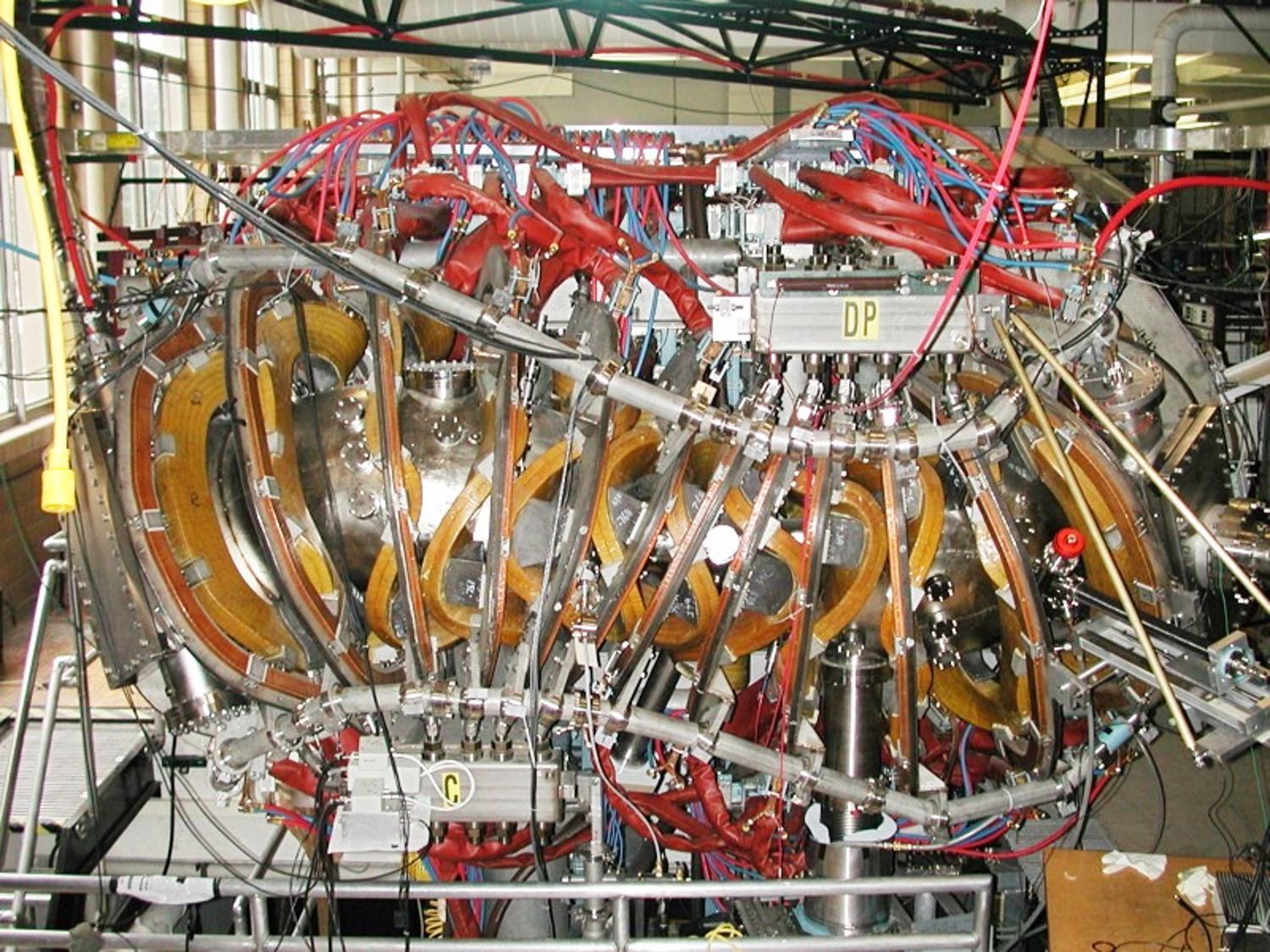
In 1971, scientists Dänner and Knobloch published their findings on nuclear fusion at the Max Planck Institute for Plasma in Munich, Germany. Since then, other scientists around the world have dedicated their lives to designing and building a reactor that will allow for continuous and safe nuclear fusion.
Over the past 50 years, six different nuclear fusion reactors have been built: The Reversed-Field Pinch (RFP), the Magnetized Target Fusion (MTF), the Inertial Confinement Fusion (ICF), the Stellarators, Tokamak Reactors, and Spherical Tokamak Reactors.
Each Kind of Reactor Is Using Different Tactics to Achieve the Same Results
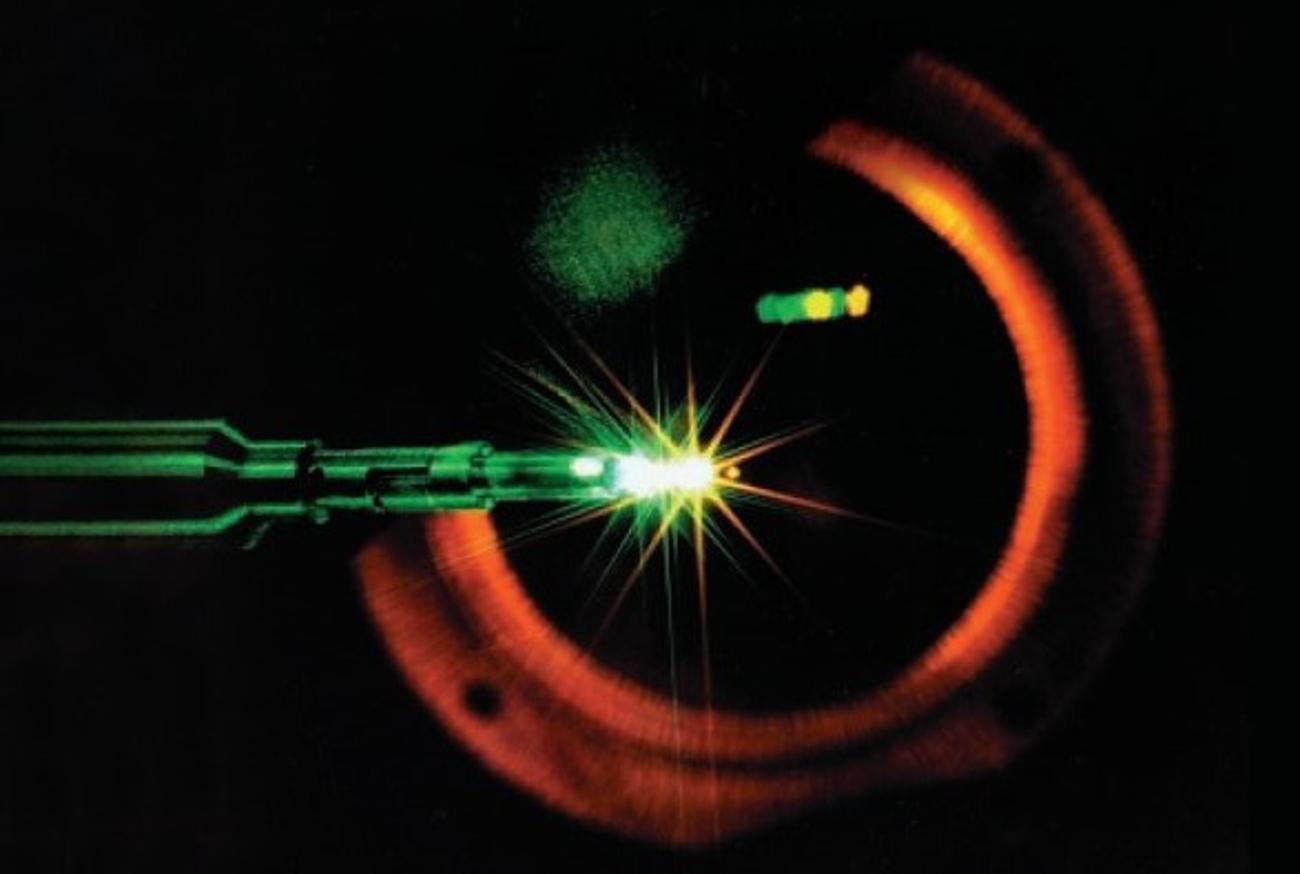
Technically, each kind of reactor is working toward creating consistent and manageable nuclear fusion; however, they use different designs and tactics to do so.
For example, while the Inertial Confinement Fusion method rapidly compresses nuclear fuel with the heat of high-power lasers, the Magnetized Target Fusion relies on magnetic confinement and inertial confinement fusion to produce nuclear energy.
The International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor Is Working on Tokamak Reactors
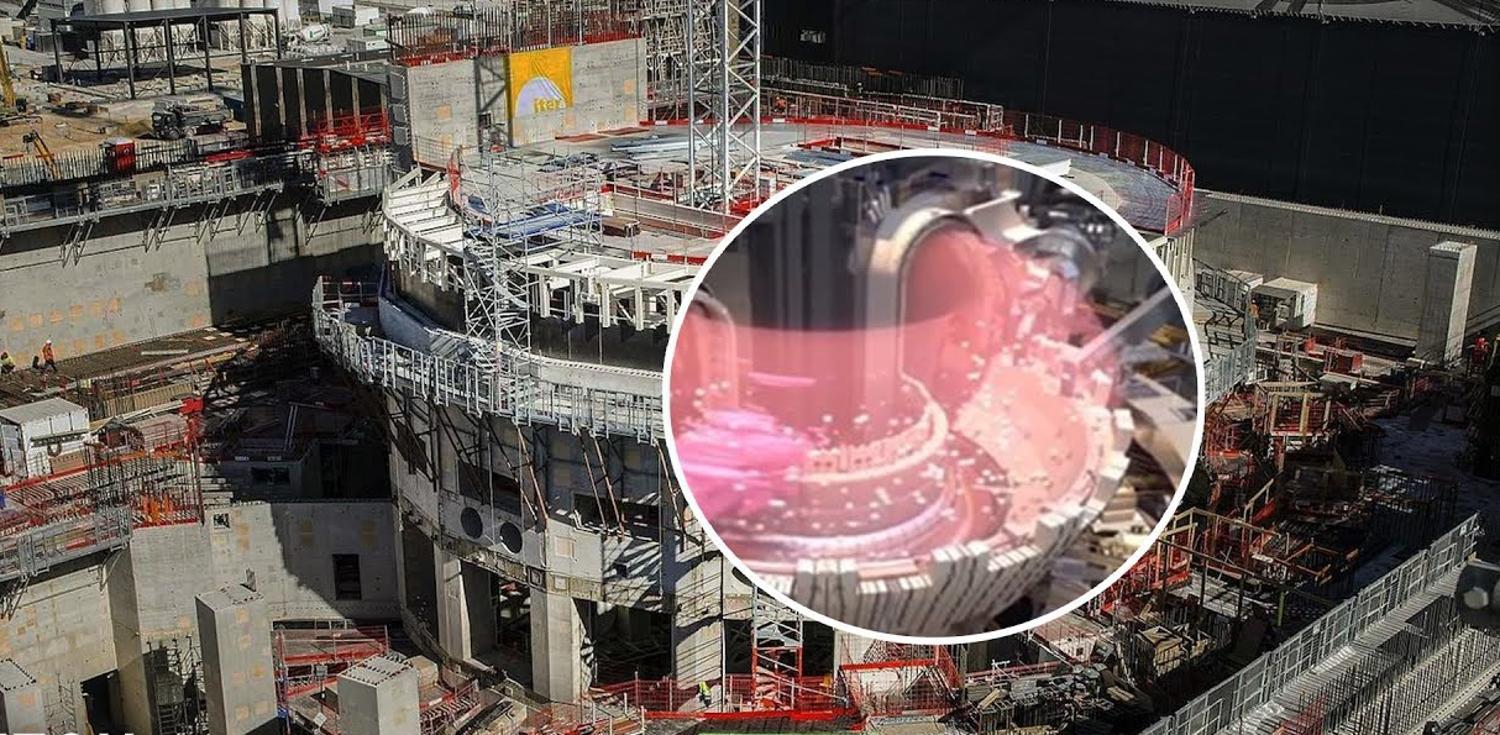
The International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) is an international nuclear fusion research center in France where scientists have been working tirelessly on perfecting the Tokamak Reactor.
It is the world’s largest nuclear fusion project, with scientists and funding from 35 different countries working together to finalize the ITER Tokamak Reactors. And finally, they have announced a wildly exciting breakthrough.
The ITER Tokamak Can Now Function for 6 Minutes
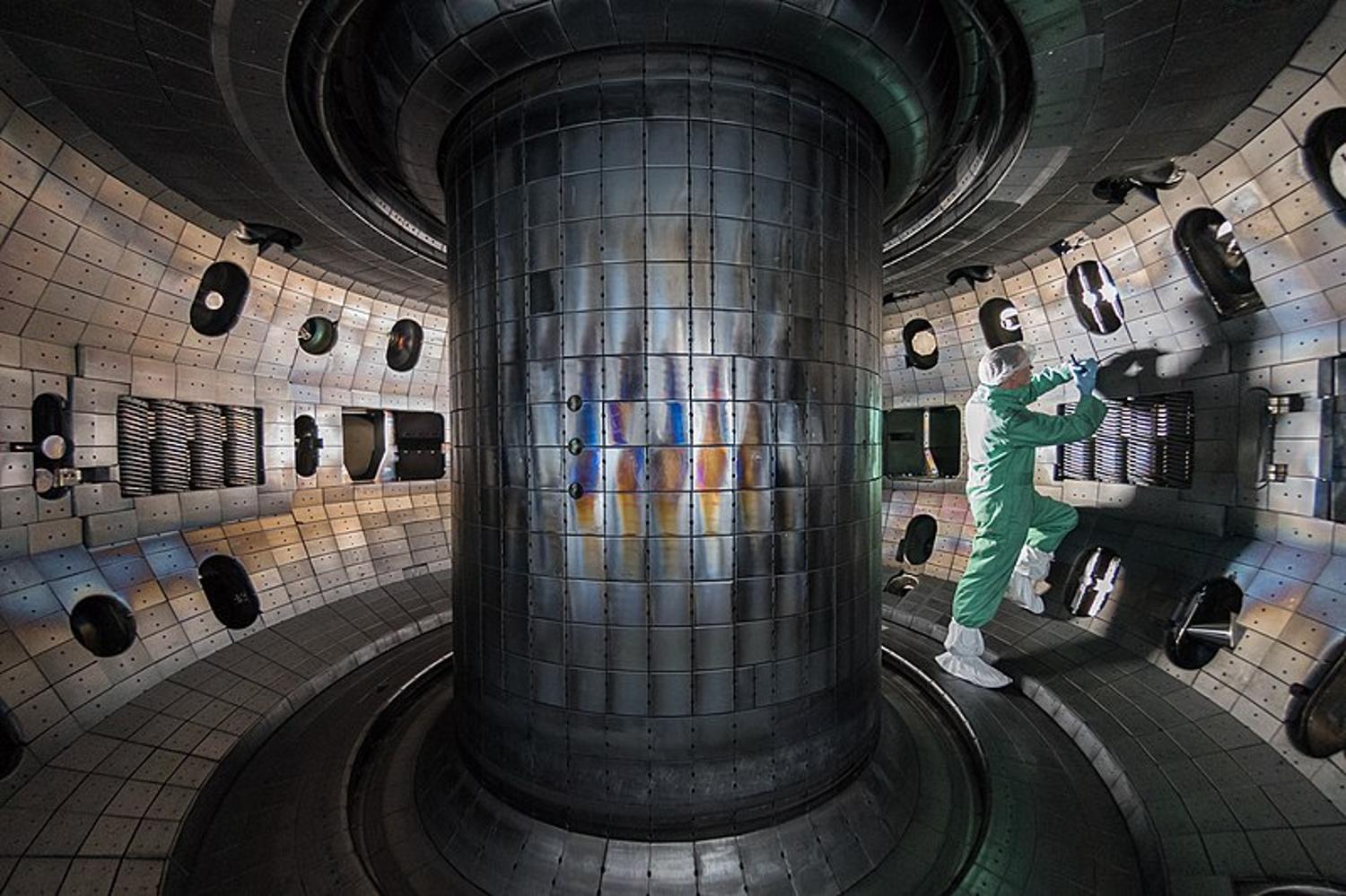

Scientists at the ITER announced that they were able to safely use their Tungsten Environment in Steady-state Tokamak for exactly 6 minutes.
Researchers noted that throughout those 360 seconds, the reactor maintained a plasma temperature of 122 million °F and an energy output of 1.15 gigajoules. For comparison, that’s 15% more energy and twice the density of any previous nuclear fusion record on Earth.
Scientists Need to Find a Way to Increase the Tokamak’s Time to 24 Hours

A spokesperson from the International Atomic Energy Agency reported “These are wonderful results;” however, they still have a lot of work to do developing the reactor to get to the point where it can be considered a consistent and sustainable energy force.
The theory among nuclear scientists all around the world is that if they can maintain this level of nuclear fusion for 24 hours, they will be able to confidently say that nuclear fusion is the new energy source of the future.
Could Nuclear Fusion Save the Planet?

This breakthrough is, of course, wildly exciting for scientists around the world, but it’s also big news for environmentalists and anyone who cares about the planet we live on.
If they can actually find a way to successfully harness the natural energy of the stars through nuclear fusion, it absolutely will be the sustainable energy of the future.
If Nuclear Fusion Is the Energy of the Future, Everything Will Change

However, that doesn’t mean the transition will be quick or easy. Everything we use, from cars and trains to electricity, heating, cooking, and everything in between, is powered by fossil fuels.
If nuclear energy is the future, everything will have to change and the world will likely look drastically different than it does now.
Economic Growth Through New Industries
The introduction of nuclear fusion energy could lead to significant economic growth by creating new industries and job opportunities.
As fossil fuel industries decline, investments in fusion technology and related sectors could drive innovation and economic diversification.
Stabilizing Energy Prices Globally

Nuclear fusion’s potential to provide a virtually limitless energy source could stabilize energy prices, reducing the economic volatility associated with fossil fuel markets.
This stability would benefit both developed and developing economies, fostering, in theory, a more global economic resilience.
Infrastructure Investments and Job Creation

The transition to nuclear fusion energy would require substantial infrastructure investments, from building reactors to upgrading the power grid.
These projects would create jobs and stimulate economic activity, boosting local and national economies.
Overcoming Extreme Conditions

Unsplash
One of the primary challenges in nuclear fusion technology is maintaining the high temperatures and pressures needed for fusion reactions.
Advances in materials science, such as developing heat-resistant materials, are crucial to overcoming this hurdle.
Achieving Net Positive Energy Output

Another significant challenge is achieving net positive energy output, where the energy produced by the fusion reaction exceeds the energy input.
Innovations in reactor design, such as more efficient magnetic confinement systems, are essential to achieving this goal.
Breakthroughs in Reactor Technology

Recent breakthroughs, like the development of more powerful superconducting magnets, have brought scientists closer to sustainable nuclear fusion.
These innovations not only improve reactor performance but also reduce operational costs, making fusion energy more economically viable.
Revolutionizing Space Exploration

Nuclear fusion energy could totally change the game for space exploration by giving spacecraft a compact and efficient power source.
This could enable longer missions and potentially even support human habitation on other planets.
Advancing Industrial Manufacturing

In the field of advanced manufacturing, nuclear fusion could provide a reliable and clean energy source for energy-intensive processes, such as metal production and chemical synthesis.
This would reduce the environmental impact of industrial activities.
Enhancing Medical Research
Nuclear fusion could also play a role in medical research by providing high-energy particles for advanced imaging and cancer treatment technologies.
This could lead to more effective diagnostic tools and therapies, improving healthcare outcomes.
Consistent Energy Supply

Compared to advanced solar power, nuclear fusion offers the advantage of being unaffected by weather conditions and daylight hours.
Fusion reactors can provide a consistent and stable energy supply, complementing intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind.
Geographic Flexibility of Fusion

Unlike geothermal energy, which is geographically limited to areas with significant volcanic activity, nuclear fusion can be implemented anywhere in the world.
This geographic flexibility makes fusion a more universally applicable energy solution.
Many Potential Applications

The applications and benefits of nuclear fusion are vast and varied, ranging from advancing industrial manufacturing to enabling deep space exploration.
While significant challenges still remain in achieving controlled and sustainable nuclear fusion reactions, continued research and investment in this field could lead to groundbreaking advancements in various industries.








































