Researchers have just discovered that preventing dementia can begin as early as childhood. A study shows that 14 risk factors newly identified that could take a massive step in reducing global incidents of dementia by a half.
Several risk factors like alcohol abuse, smoking, and excess weight can be easily avoided by most people, and doctors suggest that small life style changes could be the biggest factor in preventing mental health decline in old age.
Alzheimer’s Conference Presented the Findings

The Alzheimer’s Association International Conference was held between July 28 and August 1 in Philadelphia.
New information was presented that shows how prevention, intervention, and care can drastically reduce the risk factors of contracting cognitive decline. Billions of dollars could be saved in the healthcare field on people living longer and healthier lives as a result.
What is Dementia?
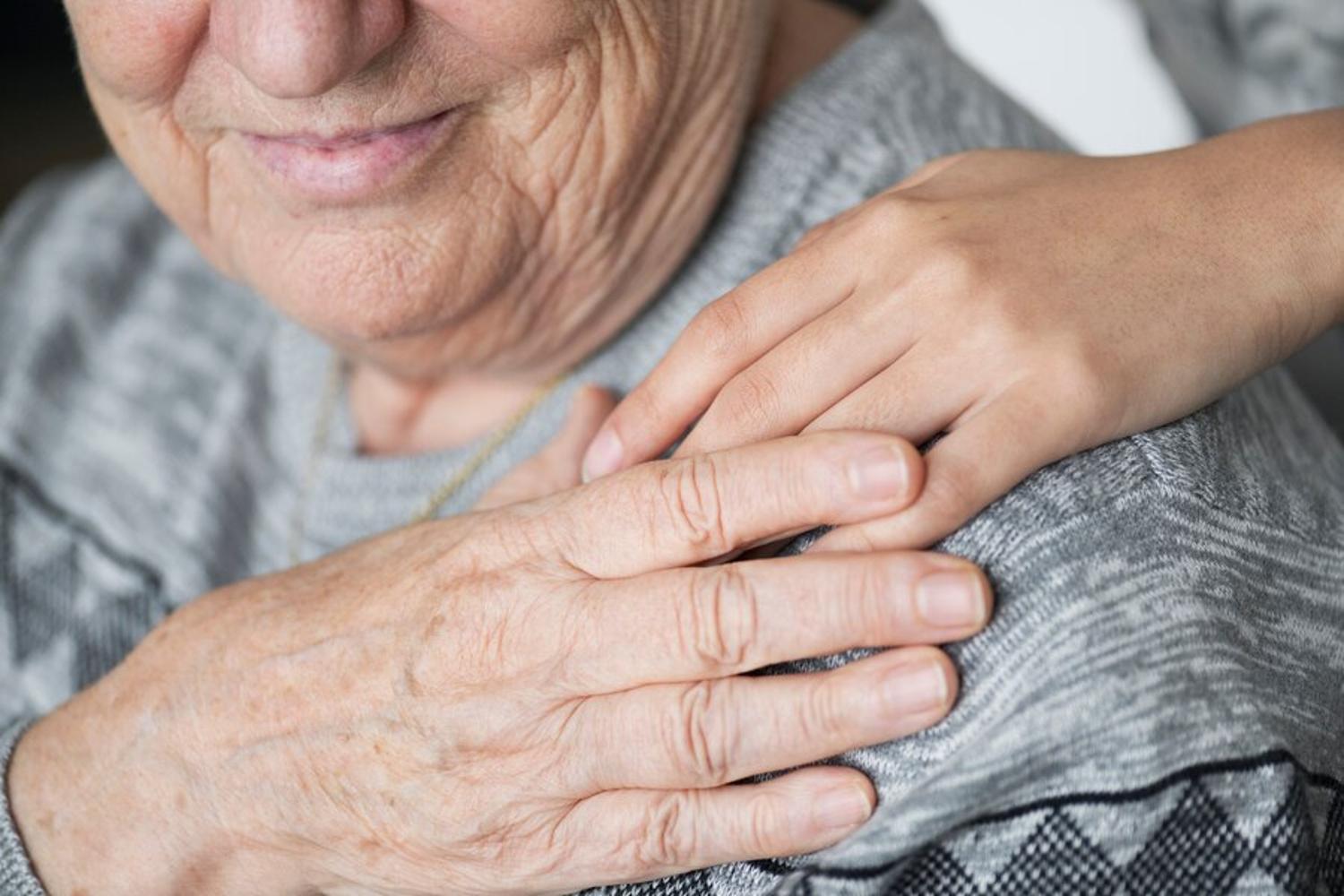

Dementia is actually an umbrella term of various diseases and symptoms. The general issues include loss of memory and other thinking abilities that are sever enough to interfere with everyday life.
Some of the diseases included are Alzheimer’s, vascular, frontotemporal, Huntington’s and more.
14 Risk Factors for Dementia

There are 14 total risk factors that are linked to more than 40% of all dementia cases.
They include: alcohol abuse, smoking, diabetes, obesity, high blood pressure, air pollution, brain injury, physical inactivity, depression, social isolation, hearing loss, lower levels of education, vision loss, and high cholesterol.
Some Risk Factors Are More Dangerous
The Commission’s report added that a few of the items on the list are more dangerous than others.
For example, high cholesterol after the age of 40 and vision loss can increase the risk of contracting demential by 9%.
Rapidly Aging Population

Due to better life-long health care, cleaner water, and more leisurely lifestyles, people are living much longer than they used to. As a result, older generations are using healthcare facilities and resources at much higher rates that what can be kept up with.
Now, the number of people with dementia is expected to triple by the year 2050. More than 57 million people suffered from the disease in 2019 and it will rise to roughly 153 people.
Health Policies Must Tackle Risk Factors

Public health safety initiatives will need to take these risk factors seriously if they want to save lives and reduce strain on the healthcare system.
The Commission report showed that lower-income countries are surging in dementia cases as the life expectancy increases. The world is estimated to spend more than $1 trillion a year on the growing issue.
Seniors Need To Stay Active
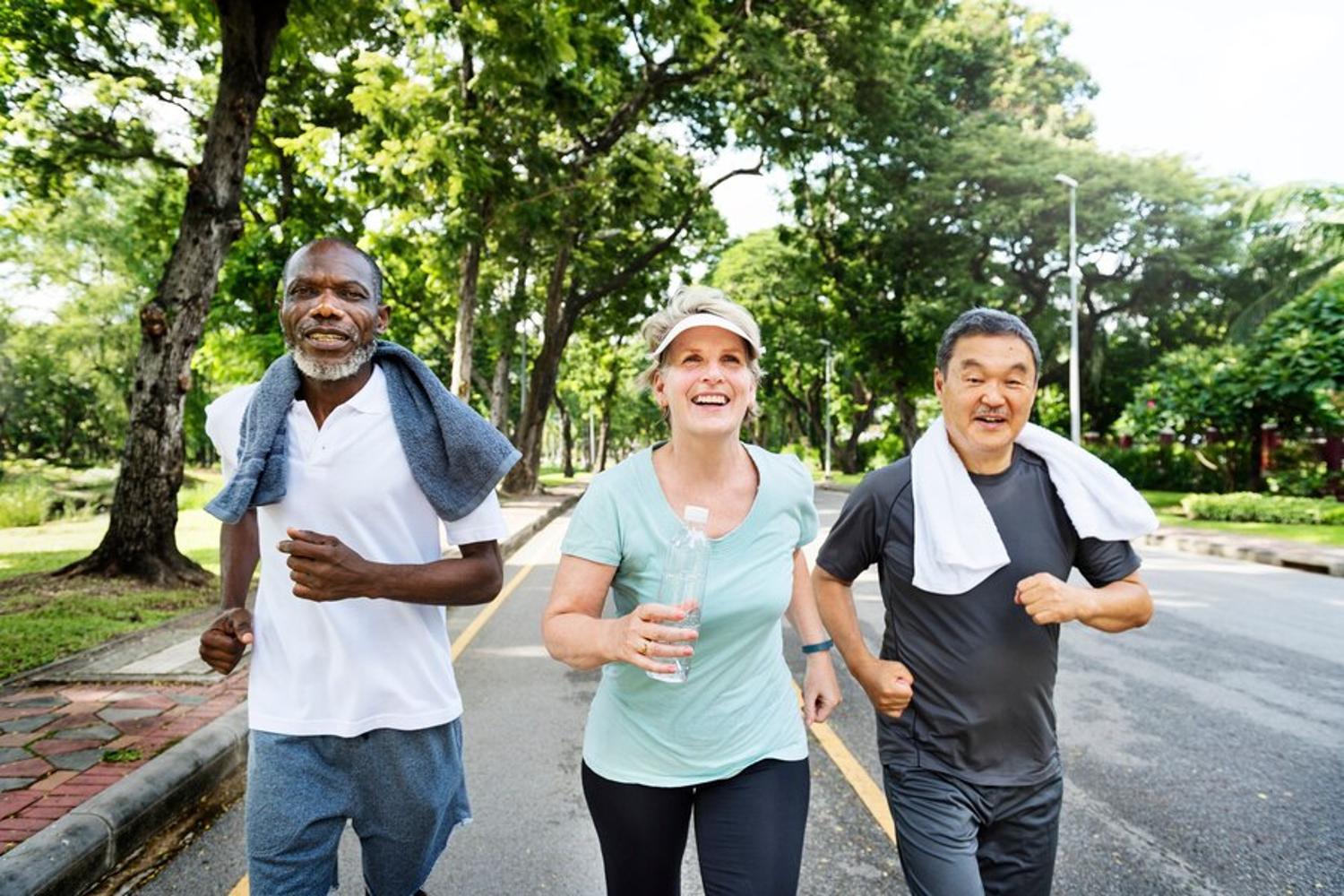

To help reduce some of the risk factors, such as social isolation, alcohol abuse, lack of physical activity, and lack of mental stimulation, the Commission also suggested keeping seniors active even into their old age.
Keeping the brain healthy and developing throughout life, people need to stay active in their communities. Participating in group activities and personal hobbies is a great way to stave off cognitive decline.
Social Isolation

Vivek H. Murthy, the U.S. Surgeon General has also issued a statement on the “epidemic of loneliness.”
He likened the issue to being just as bad as substance abuse and obesity: “Everything, from longevity to healthy brain aging, has been tied to the richness of our social connections. Psychiatry, as a field, has practiced using a biopsychosocial model of care for decades, [and] it’s good to see neurologists following our lead in recognizing the importance of social activities in healthy brain aging.”
Alcohol Abuse
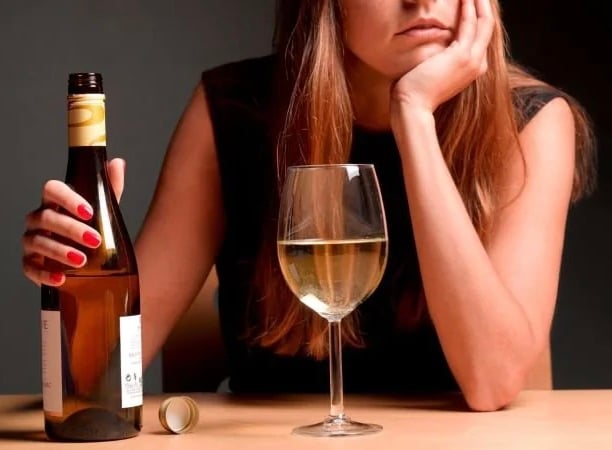

Currently, the younger generations in the United States drink much less than previous ones did.
There is a growing consensus that ingesting even small amounts of alcohol can have long term and serious health consequences. Physical and mental decline are both related to drinking alcohol. “Heavy alcohol use is one modifiable risk factor for dementia. This can be heavy daily use or also periodic episodes of binge drinking. Both are detrimental to the health of the brain with aging,” he said.
Air Pollution

Unfortunately, there are some risk factors that many people can’t avoid.
Air pollution and radio waves from cell phones and transmission wires have been directly linked to the increased incidence of dementia in current elderly generations.
Low Income Areas

People living in lower income areas have a difficult time getting out into nature, moving away from pollution and toxins and relaxing for their mental health.
Improving global poverty will go a long way to decrease the incedence of worldwide dementia.








































