A new case of sexually transmitted ringworm, caused by the rare fungus Trichophyton mentagrophytes type VII, has been reported in the U.S. for the first time.
This case is raising concerns among health experts due to its resistance to common treatments. As fungal infections become harder to treat, understanding and awareness are critical.
The Case Details

The case involves a New York City man in his 30s who developed a red, itchy rash on his legs, groin, and buttocks after traveling to England, Greece, and California.
He reported having sex with multiple men during his trip. Despite the rash, his sexual partners did not show any signs of ringworm.
Identification of the Fungus

Tests revealed that the man had contracted Trichophyton mentagrophytes type VII, a strain of fungus previously reported in France. This marks the first time this specific fungus has been identified in the United States.
The infection was confirmed through lab tests after the man sought medical help for his persistent symptoms.
The Treatment Journey

The man’s infection proved resistant to initial treatments. He was first given fluconazole for four weeks without improvement.
Doctors then prescribed six weeks of terbinafine, followed by approximately eight additional weeks of itraconazole. The combination of these treatments finally cleared the infection after four and a half months.
Expert Opinion

Dr. Avrom Caplan of NYU Grossman School of Medicine, the lead author of the case report, stated, “There’s no evidence that this is widespread, but it’s important for people to be aware and seek treatment if they have persistent rashes.”
He encourages individuals to consult a doctor if they notice symptoms that do not improve.
Importance of Fungal Resistance

Mahmoud Ghannoum, a professor of dermatology, emphasized the significance of this case. He noted, “We think a lot about antibacterial resistance, but this is a very important time for us to think about anti-fungus resistance.”
This case shows the need for heightened awareness and new treatment strategies for fungal infections.
Comparison to Eczema
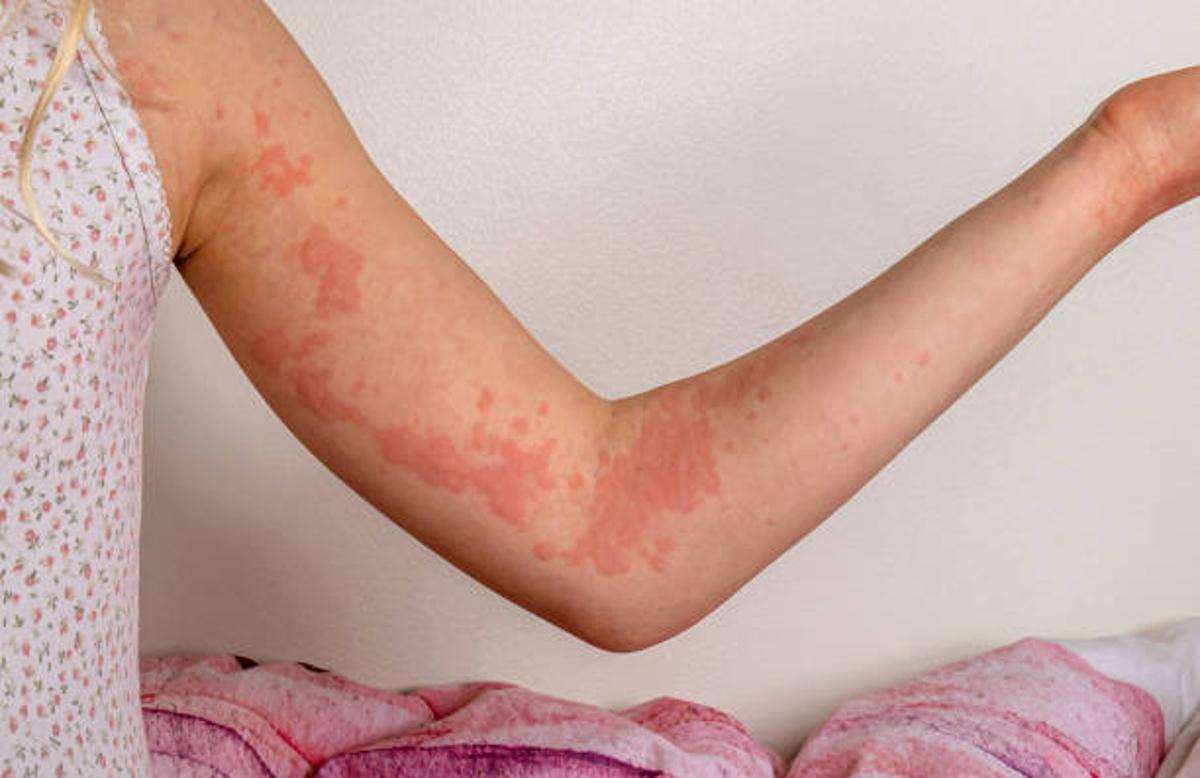
The rash caused by this infection may resemble an eczema flare rather than the typical ringworm that forms in circles. This can make it harder to diagnose without proper testing, leading to delays in appropriate treatment.
The infection is not life-threatening but can cause permanent scarring if not treated correctly.
Transmission and Risk Factors

While the infection was likely transmitted through sexual contact, it’s also possible it was contracted in a sauna visited by the man two months before symptoms appeared.
This highlights the need for awareness of various transmission routes for fungal infections, including both direct contact and environmental exposure.
Previous Cases and Drug Resistance
Caplan’s team has identified other cases of drug-resistant ringworm in New York City, involving both men and women. These cases, caused by Trichophyton indotineae, are not sexually transmitted but are highly contagious and resistant to treatment.
This growing trend raises concerns about the spread and treatment of fungal infections.
CDC’s Warning to Clinicians

Jeremy Gold from the CDC advises clinicians to consider fungi as potential causes of sexually transmitted diseases.
He stressed that many patients receive multiple courses of ineffective antibacterial treatments before the correct diagnosis is made, delaying effective care and prolonging patient suffering.
Encouraging Prompt Treatment

Caplan urges individuals with persistent rashes to seek medical attention promptly. He says, “If you have a rash or lesions on your skin that aren’t getting better, and you think it might be ringworm, see your doctor.”
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to managing these infections and preventing long-term complications.
Future Implications

This rare case of sexually transmitted ringworm serves as a wake-up call for the medical community. Ongoing research and increased awareness are essential to address the challenges posed by resistant fungal infections.
Health experts stress the importance of considering fungal infections in diagnoses to ensure timely and effective treatment.








































